BREAKING: 9 States Manipulating Weather with Cloud Seeding!
Understanding Cloud Seeding: Weather Modification in the United States
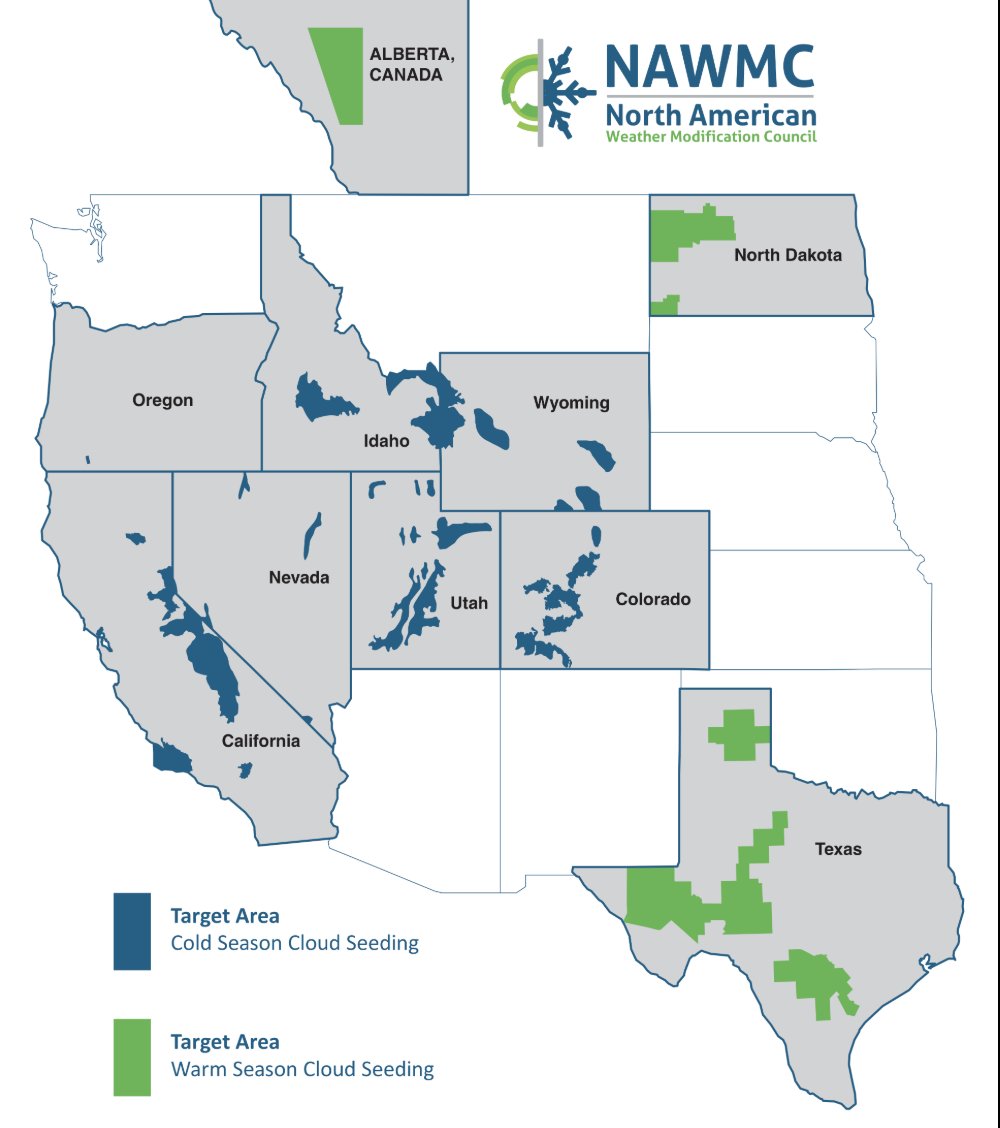
Cloud seeding has emerged as a significant weather modification technique, actively employed in several U.S. states to enhance precipitation and combat drought conditions. As highlighted in a recent tweet, nine states—Texas, California, Utah, Colorado, Nevada, Idaho, Wyoming, New Mexico, and North Dakota—are currently engaging in this practice. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cloud seeding, its methodologies, benefits, and the implications of its use.
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a form of weather modification that involves dispersing substances into the atmosphere to encourage precipitation. The primary materials used in cloud seeding include silver iodide, sodium chloride (table salt), and liquid propane. These substances serve as nuclei around which moisture can condense, forming raindrops or snowflakes.
The process typically involves aircraft equipped to release these materials into targeted clouds, or ground-based generators that can send particles into the atmosphere. The goal is to stimulate precipitation in areas that may be experiencing drought or to increase snowpack in mountainous regions for water supply.
States Actively Engaged in Cloud Seeding
As mentioned in the tweet, the following nine states are currently employing cloud seeding techniques:
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
Texas
Texas has a long history of cloud seeding, particularly during drought conditions. The Texas Water Development Board oversees cloud seeding operations, which aim to increase rainfall and address water shortages.
California
California frequently relies on cloud seeding to enhance water supplies, especially given its recurring drought cycles. The state’s Department of Water Resources has implemented several cloud seeding projects to bolster precipitation during critical dry periods.
Utah
Utah utilizes cloud seeding to improve snowpack in the Wasatch Range, which is vital for the state’s water supplies. The Utah Division of Water Resources manages these operations to ensure the availability of water for agriculture and urban use.
Colorado
Colorado has initiated cloud seeding programs to augment water resources in the face of increasing demand and diminishing supplies. The state’s water conservation efforts have integrated cloud seeding as a viable solution to tackle water scarcity.
Nevada
Nevada employs cloud seeding to enhance precipitation, especially in the Sierra Nevada mountains. This practice helps replenish the state’s reservoirs and supports local ecosystems.
Idaho
Idaho has been actively involved in cloud seeding for several decades, focusing on increasing snowpack levels and improving water availability for agriculture and hydroelectric power generation.
Wyoming
Wyoming’s cloud seeding efforts are aimed at increasing snowfall in mountainous areas, which is crucial for water supply. The state has collaborated with neighboring regions to optimize the benefits of cloud seeding.
New Mexico
New Mexico has implemented cloud seeding projects to address water shortages and enhance rainfall in arid regions. The state’s climate variability makes cloud seeding an important tool for water management.
North Dakota
North Dakota has also embraced cloud seeding to modify weather patterns, particularly to increase rainfall during dry spells. The state conducts cloud seeding operations to ensure agricultural productivity.
Benefits of Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding presents several potential benefits, particularly in regions prone to drought:
- Increased Precipitation: By stimulating rainfall, cloud seeding can effectively mitigate the impacts of drought, ensuring water availability for agriculture and domestic use.
- Enhanced Snowpack: In mountainous regions, cloud seeding can help boost snowpack levels, which serve as a critical water source during the warmer months when melting snow feeds rivers and reservoirs.
- Water Resource Management: Cloud seeding can be integrated into broader water management strategies, providing a supplementary method to enhance water supplies in areas facing water scarcity.
- Agricultural Support: By increasing precipitation, cloud seeding can support crop production, helping farmers maintain yields during dryer seasons.
- Ecosystem Benefits: Improved rainfall can lead to more robust ecosystems, supporting wildlife habitats and biodiversity.
Concerns and Controversies
Despite its potential benefits, cloud seeding also raises several concerns:
- Environmental Impact: The long-term effects of introducing chemicals like silver iodide into the atmosphere are still under study. While deemed safe at low concentrations, some environmentalists raise concerns about potential ecological impacts.
- Effectiveness: The efficacy of cloud seeding can vary greatly depending on atmospheric conditions. Some studies suggest that cloud seeding may not always produce significant precipitation increases.
- Ethical Considerations: The manipulation of weather patterns can raise ethical questions, particularly regarding the unintended consequences for neighboring areas that may receive less rainfall as a result.
- Cost: Implementing cloud seeding programs can be expensive, necessitating careful consideration of the costs versus the benefits.
Conclusion
Cloud seeding has become an official policy in multiple U.S. states, serving as a proactive approach to weather modification amid growing concerns about water scarcity and climate change. While it offers promising benefits for increasing precipitation and supporting water resource management, it is essential to continue researching and monitoring its environmental impact and effectiveness. As states like Texas, California, Utah, and others pursue cloud seeding, understanding its implications will be crucial in addressing the challenges posed by an increasingly variable climate. By balancing the benefits and concerns associated with cloud seeding, policymakers can make informed decisions that contribute to sustainable water management practices.

9 U.S. STATES ARE USING CLOUD SEEDING TO MODIFY THE WEATHER RIGHT NOW
This isn’t a conspiracy. It’s official policy and its active.
Right now, Texas, California, Utah, Colorado, Nevada, Idaho, Wyoming, New Mexico, and North Dakota are blasting chemicals into the sky to force… pic.twitter.com/idY70rIZaa
— HustleBitch (@HustleBitch_) July 6, 2025
9 U.S. STATES ARE USING CLOUD SEEDING TO MODIFY THE WEATHER RIGHT NOW
Weather modification is no longer just a concept from sci-fi movies or conspiracy theories. It’s happening right now in the United States, as nine states actively employ cloud seeding techniques to influence weather patterns. If you’re in Texas, California, Utah, Colorado, Nevada, Idaho, Wyoming, New Mexico, or North Dakota, you might just witness this firsthand. But what exactly is cloud seeding, and why are these states so keen on modifying the weather?
This isn’t a conspiracy. It’s official policy and it’s active.
Let’s clear the air—cloud seeding is backed by science and government policies. It’s not some far-fetched idea or a secret experiment. These state governments have recognized the potential benefits of cloud seeding, from enhancing water supplies to potentially mitigating droughts. With the looming threat of climate change, many regions are looking for innovative ways to adapt, and cloud seeding is one of the strategies being explored.
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding involves dispersing substances into the atmosphere to encourage precipitation. Common materials used include silver iodide, sodium chloride (table salt), and even dry ice. These materials act as nuclei around which moisture can condense, ultimately leading to rain or snow. It’s like giving nature a little nudge to help it do what it’s supposed to do—just a bit faster.
Why Are States Investing in Cloud Seeding?
The reasons for cloud seeding vary by state, but there are a few common threads. Many states are facing severe water shortages and drought conditions. For instance, California has suffered from extended drought periods, leading to water rationing and agricultural concerns. By augmenting precipitation through cloud seeding, states hope to alleviate some of these issues.
In states like Texas and New Mexico, where agriculture is a vital part of the economy, the benefits of increased rainfall can be enormous. Farmers rely on steady rainfall to grow crops, and any additional moisture can significantly impact yield. Thus, the push for cloud seeding is often tied directly to economic stability and food security.
Which States Are Leading the Charge?
As mentioned earlier, nine states are currently using cloud seeding techniques:
- Texas: With its vast agricultural sector and frequent droughts, Texas has invested heavily in weather modification programs.
- California: Facing ongoing water issues, California actively employs cloud seeding to increase snowpack in the Sierra Nevada Mountains.
- Utah: The state has been a pioneer in cloud seeding efforts, particularly for its ski resorts and water supplies.
- Colorado: Known for its diverse landscapes, Colorado utilizes cloud seeding to boost its mountain snowpack.
- Nevada: The state supports cloud seeding initiatives to help replenish its dwindling water resources.
- Idaho: With its agricultural focus, Idaho sees cloud seeding as a way to support its farming community.
- Wyoming: The state has implemented cloud seeding projects primarily to enhance its water supply.
- New Mexico: Similar to Texas, New Mexico seeks to combat drought conditions through weather modification.
- North Dakota: The state has recognized the potential benefits of cloud seeding for agriculture and water management.
How Does Cloud Seeding Work?
Cloud seeding is typically conducted using aircraft equipped with flares that release the seeding agents into the atmosphere. The planes fly through cloud formations, targeting areas where conditions are favorable for precipitation. The process can be timed to coincide with weather patterns to maximize effectiveness. Weather modification experts closely monitor atmospheric conditions to determine the best times for cloud seeding.
In some instances, ground-based generators are used to disperse the seeding materials into the air. This method can be particularly effective for enhancing localized precipitation events.
The Science Behind Cloud Seeding
At its core, cloud seeding is based on solid meteorological principles. The science behind it involves understanding how clouds form and how precipitation occurs. For instance, clouds are made up of tiny water droplets or ice crystals that can combine to form larger droplets. When these droplets become heavy enough, they fall as rain or snow. By introducing seeding agents, scientists can help facilitate this process.
Research has shown that cloud seeding can indeed increase precipitation. According to a report by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), cloud seeding can result in a 10-30% increase in precipitation under optimal conditions. While it’s not a silver bullet for drought, it can provide valuable support to water management efforts.
Potential Benefits of Cloud Seeding
The benefits of cloud seeding are numerous:
- Increased Water Supply: The most immediate benefit is the potential increase in water supply, which is crucial for both urban and agricultural needs.
- Drought Mitigation: By enhancing precipitation, cloud seeding can help alleviate drought conditions, providing relief to farmers and communities.
- Improved Snowpack: In mountainous regions, increased snowfall can lead to better water storage for spring and summer months.
- Economic Stability: For states heavily reliant on agriculture, the economic benefits of improved crop yields can be significant.
Controversies and Considerations
Despite its potential benefits, cloud seeding is not without its controversies. Critics argue that the long-term effects of introducing chemicals into the atmosphere are not fully understood. Concerns about environmental impacts and the ethics of weather modification are common discussions among scientists and the public alike.
Additionally, there’s the question of fairness. If certain regions are able to manipulate their weather, what does that mean for others that are not? There’s a risk of exacerbating inequalities in water distribution, leading to tensions between states and communities.
The Future of Cloud Seeding
As climate change continues to pose challenges for water resources, the conversation around cloud seeding is likely to grow. With advancements in technology and increased understanding of atmospheric science, cloud seeding may become more refined and effective.
Moreover, as more states adopt weather modification policies, it’s important to continue discussions around ethics, environmental impacts, and equitable distribution of resources. The balance between innovation and responsibility will shape the future of cloud seeding in the United States.
Final Thoughts
In summary, cloud seeding is a fascinating blend of science and policy that’s currently being utilized by several states in the U.S. With its potential to increase precipitation and support agriculture, it’s a tool that could help address pressing water issues. While it brings with it a host of considerations and controversies, the impact of cloud seeding on the future of weather modification is certainly one to watch.
“`