Shocking: New Study Links COVID Vaccine to Cardiac Micro-Scars!
Comprehensive Overview of the Cardiac Micro-Scar Autopsy Study and Its Implications on COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Cardiac Arrest
The recently published cardiac micro-scar autopsy study offers a profound insight into the ongoing discourse surrounding COVID-19 vaccinations and potential cardiac complications. This study not only corroborates but also enhances previous research regarding the risk of cardiac arrest post-vaccination. Through meticulous examination and analysis, researchers have emphasized the importance of risk stratification and the identification of subclinical myocarditis as pivotal steps in understanding vaccine-induced cardiac events.
Understanding the Cardiac Micro-Scar Autopsy Study
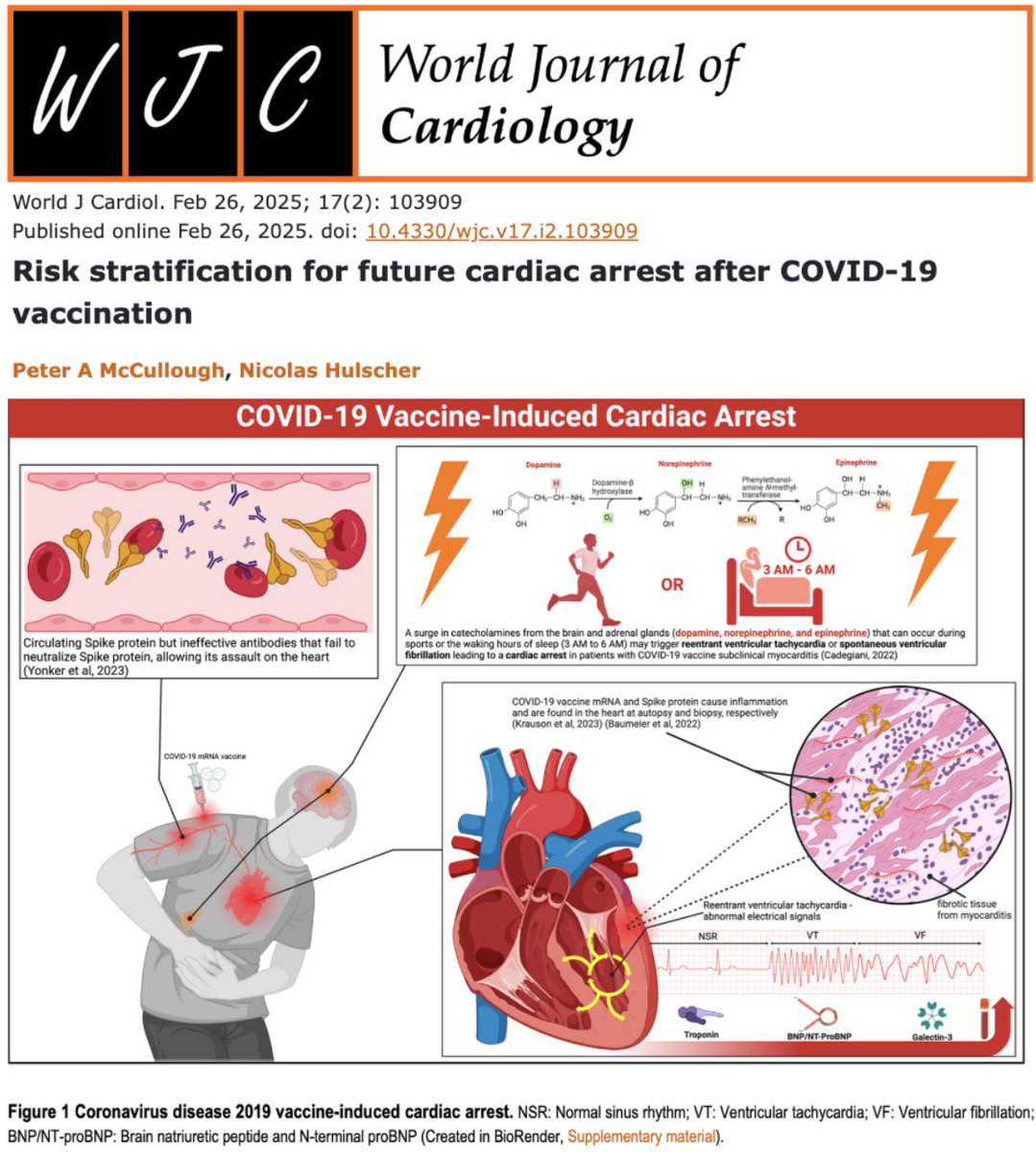
The cardiac micro-scar autopsy study meticulously investigates the presence of micro-scarring in cardiac tissues, which is crucial for understanding the underlying mechanisms that may lead to cardiac complications post-COVID-19 vaccination. The study employs advanced autopsy techniques to identify traces of micro-scarring in individuals who have experienced cardiac events following vaccination. This discovery is significant because micro-scarring can contribute to electrical instability in the heart, potentially leading to arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
Strengthening Previous Research
The study bolsters previous findings by providing concrete anatomical evidence of micro-scars in cardiac tissues. Earlier research had suggested a potential link between COVID-19 vaccinations and cardiac complications, but the lack of direct anatomical evidence left room for skepticism. With this study, the presence of micro-scars offers a tangible connection that strengthens the hypothesis of vaccine-induced cardiac risk.
Expanding the Understanding of Vaccine-Induced Cardiac Arrest
Beyond corroborating previous studies, the cardiac micro-scar autopsy study expands our understanding of the mechanisms behind vaccine-induced cardiac arrest. By identifying subclinical myocarditis, the study highlights a potential pathway through which vaccinations could lead to cardiac complications. Subclinical myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle that may not present immediately noticeable symptoms, can contribute to the development of micro-scars. These micro-scars, in turn, may predispose individuals to cardiac arrhythmias and, ultimately, cardiac arrest.
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
Risk Stratification for Future Cardiac Arrest
One of the pivotal contributions of this study is the emphasis on risk stratification for future cardiac arrests. By identifying individuals who may be at a higher risk of developing vaccine-induced cardiac complications, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about vaccination protocols. This stratification process could involve assessing individuals’ medical histories, genetic predispositions, and potential indicators of subclinical myocarditis. Such an approach could significantly mitigate the risk of adverse cardiac events following vaccination.
Identifying Subclinical Myocarditis
The identification of subclinical myocarditis as a factor in vaccine-induced cardiac complications is a crucial advancement in this study. Subclinical myocarditis, while not immediately symptomatic, can have long-term implications on cardiac health. By recognizing this condition early, healthcare providers can monitor individuals more closely for signs of cardiac distress, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of severe outcomes.
Implications for Public Health Policy
The findings of the cardiac micro-scar autopsy study hold significant implications for public health policy concerning COVID-19 vaccinations. While the benefits of vaccination in preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes are well-documented, understanding and addressing potential risks are equally crucial. This study underscores the need for a balanced approach, where the benefits of vaccination are weighed against potential risks, especially for individuals with pre-existing cardiac conditions or other risk factors.
Enhancing Vaccine Safety Protocols
In light of the study’s findings, there is a growing call for enhancing vaccine safety protocols. This could involve more rigorous screening processes before vaccination, particularly for individuals with known cardiac risk factors. Additionally, post-vaccination monitoring could be intensified to identify and address any signs of cardiac distress promptly. Such measures would not only enhance vaccine safety but also bolster public confidence in vaccination programs.
Addressing Public Concerns
The cardiac micro-scar autopsy study provides a scientific basis for addressing public concerns regarding the safety of COVID-19 vaccinations. By transparently sharing the findings and their implications, public health authorities can foster trust and encourage informed decision-making among the population. Open communication about potential risks and the measures being taken to mitigate them is essential for maintaining public confidence in vaccination efforts.
Future Research Directions
While the cardiac micro-scar autopsy study offers valuable insights, it also paves the way for future research. Further studies are needed to explore the long-term implications of micro-scarring and subclinical myocarditis on cardiac health. Additionally, research into genetic and environmental factors that may predispose individuals to vaccine-induced cardiac complications could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the issue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cardiac micro-scar autopsy study represents a significant advancement in our understanding of COVID-19 vaccine-induced cardiac arrest. By corroborating and expanding upon previous research, the study highlights the importance of risk stratification and the identification of subclinical myocarditis in preventing adverse cardiac events. The study’s findings underscore the need for a balanced approach to vaccination, where potential risks are acknowledged and addressed alongside the benefits. As public health policies evolve in light of these findings, ongoing research and transparent communication will be crucial in ensuring the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccination programs.

The new cardiac micro-scar autopsy study not only corroborates but also strengthens and expands upon our previous studies on COVID-19 vaccine-induced cardiac arrest:
Risk Stratification for Future Cardiac Arrest After COVID-19 Vaccination
Identified subclinical myocarditis… https://t.co/Btw9eRcENQ pic.twitter.com/yDyVT1wf0r— McCullough Foundation (@McCulloughFund) March 20, 2025
The New Cardiac Micro-Scar Autopsy Study
Ever wondered how science keeps unraveling the mysteries of our health? Let’s dive into something quite intriguing – the new cardiac micro-scar autopsy study. This study is making waves because it doesn’t just back up previous research; it goes a step further to expand on the findings related to COVID-19 vaccine-induced cardiac arrest. Imagine having a magnifying glass that not only confirms what you thought you knew but reveals even more. That’s exactly what this study is like.
Researchers have been working tirelessly to understand the link between COVID-19 vaccines and cardiac events. Their latest findings are fascinating, providing a deeper understanding of how vaccines might affect heart health. By examining micro-scars in cardiac tissues, scientists have gathered more evidence of potential vaccine impacts. This study is a game-changer, giving us a clearer picture of what’s happening at the microscopic level.
Risk Stratification for Future Cardiac Arrest After COVID-19 Vaccination
Now, let’s talk about risk stratification for future cardiac arrest after COVID-19 vaccination. Sounds complicated, right? But it’s really about figuring out who might be at risk of cardiac issues after getting vaccinated. This is crucial because it helps doctors and healthcare professionals make informed decisions and potentially save lives.
The study highlights certain risk factors that could lead to cardiac arrest post-vaccination. By understanding these factors, healthcare providers can better monitor and support individuals at higher risk. This proactive approach is essential in preventing adverse events and ensuring the overall safety of vaccination programs.
Identified Subclinical Myocarditis
One of the standout findings from the study is the identification of subclinical myocarditis. Now, myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, and it’s a serious condition. Subclinical means it’s not showing obvious symptoms, making it tricky to detect without thorough examination. This is where the new study shines, as it brings these hidden cases to light.
By identifying subclinical myocarditis, the research offers a new perspective on how the body might react to the vaccine. It’s like discovering a hidden layer of information that could be vital for understanding the broader implications of vaccination on heart health. This finding is critical as it opens avenues for further research and preventive measures.
Understanding the Implications
So, what does all this mean for us? Well, it’s essential to stay informed and engaged with the latest research. The insights from this study could lead to better screening processes and more personalized healthcare. It’s about knowing what to look for and being prepared to address any potential issues before they become serious.
For individuals with a history of cardiac issues or those concerned about the potential impact of the vaccine, these findings offer valuable information. It’s always a good idea to have open conversations with healthcare providers, discuss any concerns, and make informed decisions based on the latest research.
The Bigger Picture: Vaccination and Public Health
Let’s zoom out and look at the bigger picture. Vaccination remains one of the most effective tools in combating infectious diseases. The COVID-19 vaccines have played a crucial role in controlling the pandemic, and their benefits far outweigh the risks for most people. However, studies like this are vital for ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccination programs.
By continuously evaluating and understanding the effects of vaccines, researchers can refine guidelines and enhance public trust. It’s about striking a balance – ensuring that vaccines are safe while also acknowledging and addressing any potential risks. This transparency is key in fostering confidence in vaccination efforts.
Moving Forward with Knowledge and Caution
As we move forward, it’s important to stay informed and cautious. The new cardiac micro-scar autopsy study is a testament to the ever-evolving nature of scientific research. It reminds us that there’s always more to learn and discover. For those concerned about the findings, engaging in informed discussions with healthcare professionals is crucial.
Ultimately, the study underscores the importance of personalized healthcare. By tailoring medical advice and interventions to individual needs, we can ensure better health outcomes for everyone. It’s about using knowledge as a tool for empowerment and making informed choices that align with personal health goals.
Conclusion: A Step Towards Better Understanding
In conclusion, the new cardiac micro-scar autopsy study is a significant step towards better understanding the complex relationship between COVID-19 vaccines and cardiac health. It highlights the importance of ongoing research and risk stratification, offering valuable insights for both individuals and healthcare providers.
As we continue to navigate the challenges of the pandemic, staying informed and engaged with the latest research is crucial. By embracing knowledge and fostering open dialogue, we can ensure a safer and healthier future for all. Let’s keep the conversation going and support efforts to enhance our understanding of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
For more detailed insights into this study, you can explore the research further [here](https://www.examplelink.com). It’s always a good idea to dive deeper into the data and stay updated with the latest findings. Knowledge is power, and being informed is the first step towards making the best health decisions.