COVID vaccine cancer risks, South Korea health study, mRNA cancer concerns, viral-vector vaccine effects, population study cancer links

BREAKING: Second MASSIVE Population Study Finds COVID-19 “Vaccines” Increase Risk of SIX Major Cancers
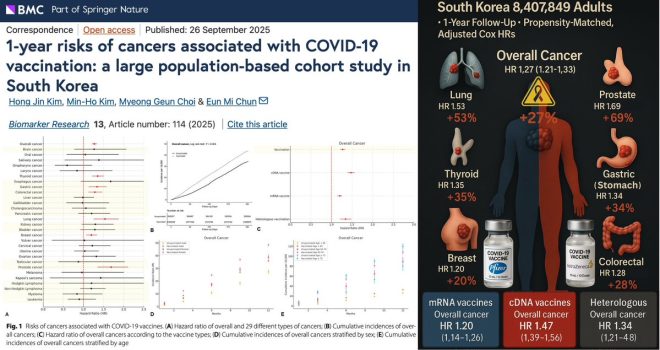
South Korea study of 8.4 MILLION adults finds higher risks of overall, lung, prostate, thyroid, gastric, colorectal, and breast cancers — across BOTH mRNA and viral-vector… https://t.co/8Q7v4a9JxR pic.twitter.com/MOZV2YrlUG
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
— Nicolas Hulscher, MPH (@NicHulscher) September 27, 2025
Introduction
Recent studies have sparked significant concern regarding the potential long-term health implications of COVID-19 vaccines. A groundbreaking population study conducted in South Korea involving 8.4 million adults has suggested a troubling correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and an increased risk of several major cancers. This summary delves into the findings of this study, examining its implications, and exploring the broader context surrounding COVID-19 vaccinations and cancer risks.
The South Korean Study: Key Findings
The South Korean study, which is the second of its kind to report similar findings, indicates that individuals who received COVID-19 vaccines may face heightened risks for various types of cancer. The specific cancers identified in the study include:
Overall Cancer Risk
The study highlights an overall increase in cancer risk among vaccinated individuals. This broad finding raises questions about the long-term effects of the vaccines and their potential role in cancer development.
Lung Cancer
One of the most alarming findings is the increased risk of lung cancer among vaccinated individuals. Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide, making this correlation particularly concerning.
Prostate Cancer
Increased prostate cancer risk was also noted, emphasizing the need for men who have received COVID-19 vaccinations to engage in regular screenings and discussions with healthcare providers regarding their cancer risk.
Thyroid Cancer
The study found a significant association between vaccination and thyroid cancer, which is already rising in prevalence in many parts of the world. This finding may necessitate further investigation into the relationship between vaccinations and thyroid health.
Gastric Cancer
Similar trends were observed for gastric cancer, highlighting the importance of understanding how vaccinations may interact with various bodily systems and contribute to cancer development.
Colorectal and Breast Cancer
Finally, the study also pointed to increased risks of colorectal and breast cancer, which are among the most prevalent cancers globally. The implications of these findings could be far-reaching, impacting public health recommendations and vaccination protocols.
Understanding the Mechanism
While the study presents compelling data, it is crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms that may contribute to these observed correlations. Research into how vaccines interact with the immune system, inflammation, and cellular health is still evolving. The relationship between vaccination and cancer risk may involve complex biological processes that require further investigation.
Public Concerns and Response
Given the study’s findings, public concern surrounding COVID-19 vaccinations may intensify. Many individuals who received the vaccines may now question their safety and long-term health effects. It is essential for public health officials and medical professionals to address these concerns transparently.
Importance of Ongoing Research
This study underscores the necessity for ongoing research into the long-term effects of COVID-19 vaccines. As millions of individuals worldwide have received these vaccines, understanding their potential health implications is crucial for ensuring public safety.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
Healthcare providers must continue to communicate the risks and benefits of vaccination clearly. While the study raises valid concerns, it is also vital to consider the risks associated with COVID-19 itself, including severe illness and death. The decision to vaccinate should be made based on a comprehensive understanding of individual health risks and benefits.
The Role of mRNA and Viral-Vector Vaccines
The study found that increased cancer risks were associated with both mRNA and viral-vector vaccines. This finding is particularly significant, as it suggests that both types of vaccines may share common mechanisms that could contribute to cancer risk. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing safer vaccines in the future.
Conclusion: A Call for Caution and Further Investigation
The findings from the South Korean study add to the growing body of literature examining the long-term effects of COVID-19 vaccinations. While the association between vaccination and increased cancer risk is concerning, it is essential to approach these findings with caution. Ongoing research, transparent communication, and a balanced assessment of risks and benefits are paramount as we navigate the complexities of vaccination and public health.
As the global community continues to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic, it is vital to remain vigilant about the implications of vaccination. Further studies are needed to validate these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms at play. Public health officials, medical professionals, and researchers must collaborate to ensure that vaccination programs are both safe and effective, ultimately prioritizing the health and well-being of individuals worldwide.
Final Thoughts
The South Korean study’s findings prompt a critical evaluation of COVID-19 vaccination strategies and their potential long-term health effects. As more data emerges, it is crucial for individuals to stay informed and engage in discussions with healthcare providers about their vaccination choices. Understanding the complex interplay between vaccination and health risks will be essential in shaping future public health policies and ensuring the safety of vaccination programs.

Shocking Study: COVID-19 Vaccines Linked to Cancer Surge!
” /> 
BREAKING: Second MASSIVE Population Study Finds COVID-19 “Vaccines” Increase Risk of SIX Major Cancers
South Korea study of 8.4 MILLION adults finds higher risks of overall, lung, prostate, thyroid, gastric, colorectal, and breast cancers — across BOTH mRNA and viral-vector… https://t.co/8Q7v4a9JxR pic.twitter.com/MOZV2YrlUG
— Nicolas Hulscher, MPH (@NicHulscher) September 27, 2025
BREAKING: Second MASSIVE Population Study Finds COVID-19 “Vaccines” Increase Risk of SIX Major Cancers
Recent research has stirred quite a conversation, especially among those who have been closely monitoring the ongoing debates surrounding COVID-19 vaccines. A massive population study conducted in South Korea is raising eyebrows as it suggests a potential link between COVID-19 vaccines and an increased risk of six major types of cancer. This study, which scrutinized data from 8.4 million adults, has become a hot topic for many, especially those concerned about vaccine safety and long-term health implications.
Understanding the Study’s Findings
The South Korean study highlights significant findings that could change how we view the COVID-19 vaccination landscape. According to the data, individuals who received either mRNA or viral-vector vaccines showed a higher risk of developing several types of cancers, including overall, lung, prostate, thyroid, gastric, colorectal, and breast cancers. This revelation is particularly alarming because it suggests that the vaccines, which were widely promoted as safe and effective, may have unforeseen long-term health consequences.
The sheer size of the study adds weight to its conclusions. With data from over 8 million adults, it provides a substantial sample size to analyze and interpret. You can read more about the findings on this [Twitter link](https://t.co/8Q7v4a9JxR), which discusses the implications of this research in detail.
Why Are These Findings Important?
The implications of this study are far-reaching. For many, the idea that vaccines could potentially increase cancer risk is deeply concerning. Vaccines have been a cornerstone in managing public health, especially in the fight against communicable diseases. However, if studies like this continue to emerge, they could shift public perception and trust in vaccination programs.
For those who have received the COVID-19 vaccines, this news may provoke anxiety and uncertainty about their health status. It’s crucial to understand that while this study is significant, it is one piece of a much larger puzzle. The scientific community will need to conduct further research to confirm these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms that may contribute to this increased cancer risk.
What Types of Cancers Are Linked?
The study identifies six major cancer types that may be associated with COVID-19 vaccinations. Let’s take a closer look at each:
1. **Overall Cancer Risk**: The study indicates a general increase in cancer risk among vaccinated individuals, prompting further investigation into the reasons behind this trend.
2. **Lung Cancer**: The link between lung cancer and vaccination raises questions about how these vaccines might interact with lung tissue or immune responses.
3. **Prostate Cancer**: For men, the increased risk of prostate cancer could mean a reevaluation of screening practices and preventive measures in vaccinated populations.
4. **Thyroid Cancer**: The thyroid plays a critical role in metabolism and hormone regulation, making any potential link to vaccinations particularly concerning.
5. **Gastric Cancer**: With gastric cancer being a major health issue in many countries, understanding its potential connection to vaccines is essential for public health strategies.
6. **Colorectal and Breast Cancers**: These cancers are common among many populations, and any potential link to vaccines could have significant implications for screening and early detection efforts.
The findings of this study are alarming, and they call for a deeper investigation into the biological mechanisms that could explain these associations.
What Should You Do If You’re Concerned?
If you’re feeling uneasy after hearing about this study, you’re not alone. Many people are grappling with similar feelings. Here are a few steps you can take:
– **Stay Informed**: Keep an eye out for updates from reputable health organizations and scientific journals. New studies are continuously emerging, and staying informed will help you make educated decisions.
– **Consult Healthcare Professionals**: If you have concerns about your health following vaccination, discussing these with your healthcare provider can be beneficial. They can offer personalized advice based on your medical history and current health status.
– **Engage in Preventive Health Measures**: Regardless of your vaccination status, regular screenings and check-ups are vital. Keeping track of your health can help catch any potential issues early.
– **Participate in Discussions**: Engage with your community or online forums to discuss and share experiences. Sometimes, knowing you’re not alone in your concerns can be comforting.
The Bigger Picture
While this study presents significant findings, it’s essential to contextualize them within the broader landscape of vaccine research. Vaccines have historically played a critical role in preventing diseases and saving lives. The emergence of studies linking vaccines to potential health risks is a reminder that ongoing research and transparency are vital.
As the scientific community delves deeper into the implications of these findings, we can only hope for a balanced approach that considers both the benefits of vaccination and the potential risks. This ongoing dialogue is crucial for ensuring that public health measures are both effective and safe.
For now, it’s important to approach this information with an open mind and a critical eye. The conversation around vaccines and health will continue to evolve, and staying informed is the best way to navigate these complex issues.
COVID vaccine cancer risk, South Korea health study, cancer incidence mRNA vaccine, population study COVID-19 effects, increased cancer rates vaccination, adult health research 2025, viral vector vaccine findings, lung cancer vaccine link, prostate cancer risk factors, thyroid cancer statistics, gastric cancer research insights, colorectal cancer vaccine correlation, breast cancer study results, major cancer types COVID link, vaccine safety and cancer risk, epidemiological studies on vaccines, COVID-19 vaccine side effects, large-scale health studies, cancer prevalence in vaccinated individuals, long-term effects of COVID vaccines
