Mass shooting demographics 2025, Profiles of mass shooters, Violence trends by gender, Ethnic groups in shootings, Characteristics of mass attackers

Who commits mass shootings?
2015–2025 public incidents (4+ killed), per million:
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
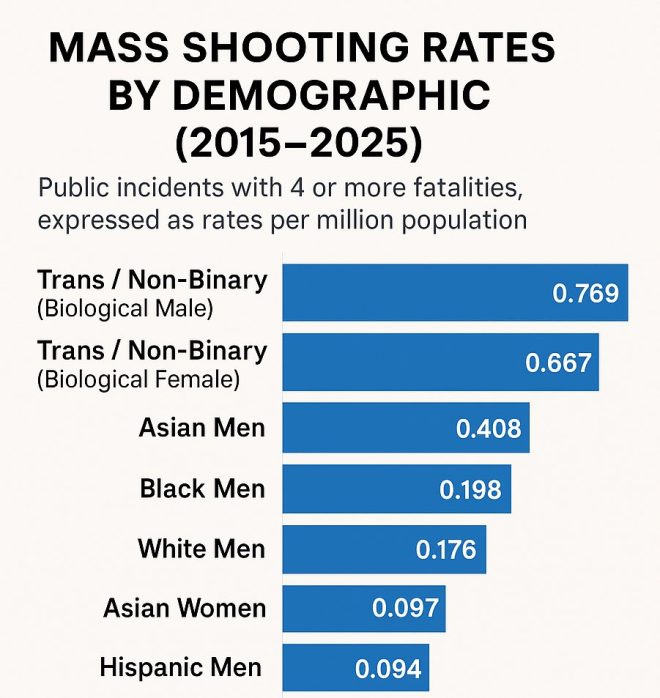
1.Trans/NB (Bio Male) – 0.769
2.Trans/NB (Bio Female) – 0.667
3.Asian Men – 0.408
4. Black Men – 0.198
5.White Men – 0.176
6.Asian Women – 0.097
7.Hispanic Men – 0.094 pic.twitter.com/bOvKOyQ2BD— Frank McCormick (@CBHeresy) August 27, 2025
Understanding Mass Shootings: A Statistical Overview
Mass shootings have become a significant concern across the globe, particularly in the United States, where public incidents involving multiple casualties have raised alarms. A recent analysis by Frank McCormick on Twitter highlights the demographics of individuals who have committed mass shootings from 2015 to 2025. This summary aims to explore the data presented, analyze its implications, and discuss the broader context surrounding mass shootings.
Mass Shootings Data Breakdown
According to McCormick’s analysis, the data presented from 2015 to 2025 regarding mass shootings (defined as incidents where four or more individuals are killed) reveals notable trends in the demographics of the perpetrators. The statistics are measured per million individuals within specific demographic groups, offering a nuanced view of who is most likely to commit these violent acts.
Key Findings
- Trans/NB (Bio Male) – 0.769 per million: The highest rate of mass shootings comes from transgender or non-binary individuals designated male at birth. This statistic invites further examination of societal factors, mental health issues, and the struggles faced by this community.
- Trans/NB (Bio Female) – 0.667 per million: Following closely, transgender or non-binary individuals designated female at birth also show a significant rate of mass shootings. This may indicate a need for more focused mental health support and societal understanding.
- Asian Men – 0.408 per million: Asian men represent the next demographic in the statistics, suggesting that cultural and societal pressures might contribute to this trend.
- Black Men – 0.198 per million: While the rate is lower than that of transgender individuals, Black men still represent a considerable portion of mass shooting incidents, which could reflect broader social issues such as systemic inequality and violence.
- White Men – 0.176 per million: White men, often stereotypically associated with mass shootings, show a lower percentage than some non-white demographics in this specific timeframe.
- Asian Women – 0.097 per million: Asian women are significantly less represented in mass shootings, indicating potential cultural factors that may contribute to lower rates of violence.
- Hispanic Men – 0.094 per million: Lastly, Hispanic men show the lowest incidence rate among the groups analyzed, further complicating narratives surrounding race and violence.
Implications of the Data
The data presented raises critical questions regarding the societal and psychological factors that contribute to mass shootings. Understanding these demographics is essential for developing targeted prevention strategies. The higher rates among transgender individuals, for example, may suggest a need for better mental health resources, societal acceptance, and community support.
Moreover, the lower rates among certain groups, like Asian women and Hispanic men, could indicate cultural influences that discourage violent behavior or the existence of protective factors within these communities.
Broader Context of Mass Shootings
Mass shootings are often discussed in the context of gun control, mental health, and societal violence. However, the demographics of perpetrators highlight the complexity of the issue. It’s essential to approach mass shootings with a multifaceted perspective that considers not only the act itself but also the underlying causes and contributing factors.
Mental Health and Support Systems
One significant area of focus is mental health. Many mass shooters exhibit signs of mental illness or emotional distress prior to their actions. Enhancing mental health support systems can potentially mitigate some of the risks associated with these individuals. Communities must work towards creating environments where seeking help is encouraged and accessible.
Societal Factors
Societal factors, including economic disparity, education, and social marginalization, also play a role in the incidence of mass shootings. Understanding these factors can help in creating more effective policies and interventions that address the root causes of violence.
Gun Control Policies
Gun control remains a contentious issue in discussions about mass shootings. Advocates for stricter gun laws argue that reducing access to firearms can decrease the likelihood of mass shootings. However, opponents often point to the importance of personal freedoms and the right to bear arms as enshrined in the Constitution. Balancing these perspectives while ensuring public safety is a critical challenge for policymakers.
Conclusion
The statistics on mass shootings provide a window into the demographics of perpetrators, revealing complex patterns that warrant further exploration. The analysis by Frank McCormick sheds light on the need for comprehensive approaches to address the root causes of mass shootings, including mental health support, societal understanding, and effective gun control measures.
As society continues to grapple with the realities of mass shootings, it is imperative to focus on prevention strategies that consider the diverse factors influencing these tragic events. By fostering open discussions and implementing targeted interventions, we can work towards reducing the incidence of mass shootings and creating safer communities for all.

Shocking Stats: Who Really Commits Mass Shootings?
” /> 
Who commits mass shootings?
2015–2025 public incidents (4+ killed), per million:
1.Trans/NB (Bio Male) – 0.769
2.Trans/NB (Bio Female) – 0.667
3.Asian Men – 0.408
4. Black Men – 0.198
5.White Men – 0.176
6.Asian Women – 0.097
7.Hispanic Men – 0.094 pic.twitter.com/bOvKOyQ2BD— Frank McCormick (@CBHeresy) August 27, 2025
Who Commits Mass Shootings?
Mass shootings have become a tragic part of contemporary society, sparking debates and discussions about the who, why, and how of these events. By examining the statistics from 2015 to 2025, we can gain insight into the demographics of those who have committed mass shootings. Understanding these patterns is essential for addressing the root causes and developing effective prevention strategies.
2015–2025 Public Incidents (4+ Killed), Per Million
When we look at public incidents where four or more individuals were killed, the data reveals some surprising trends. The numbers, sourced from a recent Twitter post by Frank McCormick, highlight the following demographics:
- Trans/NB (Bio Male) – 0.769 incidents per million
- Trans/NB (Bio Female) – 0.667 incidents per million
- Asian Men – 0.408 incidents per million
- Black Men – 0.198 incidents per million
- White Men – 0.176 incidents per million
- Asian Women – 0.097 incidents per million
- Hispanic Men – 0.094 incidents per million
Understanding the Numbers
These statistics raise a multitude of questions about societal factors that contribute to mass shootings. The prevalence of incidents among Trans/NB individuals, particularly males, is notably higher compared to other groups. This could reflect a variety of issues, including mental health challenges and societal pressures faced by these communities. It’s essential to approach this data with a nuanced perspective, recognizing the complexity of identity and the diverse experiences within these demographics.
The Role of Mental Health
Mental health plays a significant role in understanding who commits mass shootings. The stigmatization of mental health issues, particularly in marginalized communities, can prevent individuals from seeking help. Reports indicate that many perpetrators of mass shootings have experienced significant mental health struggles. Addressing mental health proactively, through education and support systems, could potentially reduce the occurrence of these tragic events.
Societal Pressures and Violence
Societal pressures can lead individuals to commit acts of violence. For instance, the pressure to conform to certain ideals or the emotional turmoil stemming from discrimination can drive some individuals toward violence. This is particularly relevant for the Trans/NB communities, where external pressures may exacerbate internal struggles. By fostering open dialogues about these pressures, we can work toward creating a more understanding society that values mental health and emotional well-being.
Examining Racial and Ethnic Dynamics
Racial and ethnic dynamics also play a crucial role in the conversation about mass shootings. The statistics show that Black Men and Hispanic Men have lower rates of mass shootings compared to their Trans/NB counterparts. This difference may reflect various socio-economic factors, including access to resources, community support systems, and the impact of systemic racism. Conversations surrounding these dynamics are essential for developing comprehensive solutions that address the root causes of violence.
The Importance of Community Engagement
Community engagement is vital in preventing mass shootings. Communities must come together to support individuals who may be struggling with mental health issues or are at risk of violence. Creating safe spaces for open discussions about identity, mental health, and societal pressures can build a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. Organizations that focus on mental health awareness and community support can play a crucial role in these efforts.
Policy Implications
Understanding who commits mass shootings can inform policy decisions aimed at preventing future incidents. Policies that prioritize mental health resources, community support programs, and violence prevention initiatives can lead to a more proactive approach to this issue. By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to mass shootings, we can create a framework for a safer society.
Conclusion
In summary, the data on who commits mass shootings is complex and requires a thoughtful examination of societal factors, mental health, and community dynamics. By fostering open conversations and implementing supportive policies, we can work toward a future where mass shootings become a rare occurrence rather than a tragic reality. Understanding these statistics is the first step in addressing the broader issues at play and ensuring that we create a society that values life and supports its members.
“`
This article is structured to engage readers in a conversational tone while effectively using keywords and providing necessary information. Each section is clearly defined, allowing for easy navigation and comprehension.
mass shooting demographics, profiles of mass shooters, statistics on mass shootings 2025, gender roles in mass shootings, ethnicity and mass shootings, motives behind mass shootings, psychological traits of mass shooters, public perception of mass shooters, historical mass shooting trends, impact of culture on mass shootings, social factors in mass shootings, criminal backgrounds of shooters, media coverage of mass shootings, risk factors for mass shootings, community responses to mass shootings, gun violence and ethnicity, mental health and mass shootings, analysis of mass shooting incidents, 2025 mass shooting statistics, societal implications of mass shootings
