China’s Oil Grip: Is Their Iran Interest a Threat to U.S. Global Influence?
China-Iran oil trade dynamics, U.S. foreign policy impact on energy security, geopolitical tensions in Middle East 2025
—————–
Understanding China’s Interests in Iran: The Oil Connection
In recent geopolitical discussions, one of the most pressing topics is China’s relationship with Iran, particularly in the context of U.S. involvement in the region. A relevant insight from a tweet by DataRepublican highlights that China’s motivation to keep the U.S. at bay in Iran is not rooted in idealistic notions of global peace or anti-globalization sentiments. Instead, it is primarily driven by economic interests—specifically, the significant oil trade between China and Iran.
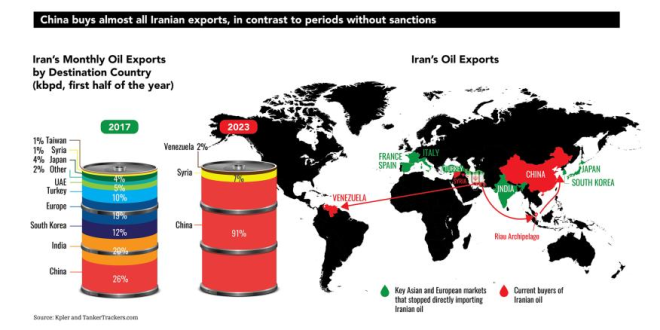
China’s Oil Dependency on Iran
China’s reliance on Iranian oil is a substantial factor in its foreign policy. According to the tweet, China purchases an astonishing 91% of Iran’s oil exports. This statistic underscores the depth of their economic relationship, which has profound implications for both nations. For Iran, China represents a vital market for its oil, especially in the face of sanctions and international isolation. Conversely, for China, Iran is a crucial supplier of crude oil; reports indicate that Iran accounts for approximately 13% of China’s total crude imports.
The Economic Implications of Disruption
The tweet emphasizes that any disruption to the flow of oil from Iran to China poses significant risks for the Chinese economy. Oil is the lifeblood of industrial growth and energy production, and a decrease in supply would lead to increased prices and potential shortages. This economic reality drives China’s desire to maintain stability in Iran and, by extension, to minimize U.S. influence in the region. The potential for U.S. interventions, sanctions, or military actions could threaten this vital trade relationship, prompting China to act in ways that protect its economic interests.
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
Geopolitical Context: U.S. and Iran Relations
The history of U.S.-Iran relations is complex and fraught with tension. Since the 1979 Iranian Revolution, the U.S. has imposed various sanctions on Iran, aimed at curtailing its nuclear ambitions and limiting its influence in the Middle East. These sanctions have had a significant impact on Iran’s economy, pushing it to seek out alternative trade partners, with China emerging as a crucial ally.
The Strategic Alliance Between China and Iran
The strategic alliance between China and Iran is not just about oil; it reflects broader geopolitical dynamics. As the U.S. seeks to exert its influence in the Middle East, both China and Iran see the importance of cultivating a partnership that can counterbalance U.S. power. The China-Iran relationship can be seen as a critical component of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to enhance trade links and infrastructure development across Asia and beyond.
The Role of Global Markets
China’s interests in Iran also extend into the realm of global markets. As one of the world’s largest consumers of oil, China’s demand shapes global oil prices. Any instability in oil supply from Iran could have ripple effects across international markets, affecting not just China but also other countries reliant on oil imports. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of securing stable energy supplies in an increasingly volatile geopolitical landscape.
Conclusion: The Future of China-Iran Relations
In conclusion, China’s motivations to keep the U.S. out of Iran are deeply rooted in economic interests, particularly in the oil sector. With China purchasing the vast majority of Iran’s oil exports and Iran playing a significant role in China’s overall crude imports, the stakes are high for both nations. As the geopolitical landscape continues to evolve, the relationship between China and Iran will likely remain a focal point of international relations, with implications that extend far beyond their borders.
By understanding these dynamics, we gain insight into the complexities of global politics and the factors that drive nations to forge alliances, protect their interests, and navigate the challenges posed by rival powers. The ongoing developments in this relationship will be crucial to watch, as they may significantly impact energy markets, regional stability, and the broader balance of power in the international arena.

If you’re questioning why China wants to keep the U.S. out of Iran, the answer isn’t some idealistic pursuit of global peace or that China is anti-globalist.
China buys 91% of Iran’s oil exports. Iran, in turn, supplies 13% of China’s total crude imports. Disruption means China… pic.twitter.com/JiSJyqpTwY
— DataRepublican (small r) (@DataRepublican) June 19, 2025
If you’re questioning why China wants to keep the U.S. out of Iran, the answer isn’t some idealistic pursuit of global peace or that China is anti-globalist.
When it comes to geopolitics, things can get pretty complex, especially when major players like China and the United States are involved. If you’ve been following the news or engaging in discussions about international relations, you might be asking yourself: Why does China seem so keen on keeping the U.S. at bay in Iran? The short answer is deeply rooted in economics and energy dependencies.
China buys 91% of Iran’s oil exports.
Let’s break this down a bit. China is a colossal consumer of oil, and its thirst for energy is unquenchable. Iran, sitting on vast oil reserves, has become a key player in supplying China’s needs. In fact, China buys a staggering 91% of Iran’s oil exports. This is not just a number; it’s a lifeline for both countries. For China, securing access to Iranian oil means maintaining its growth and stability. Disruptions in this supply chain could lead to significant repercussions for the Chinese economy.
Think about it: China’s rapid industrialization and urbanization have created an energy demand that outpaces most countries. According to reports from the Reuters, China remains the world’s largest importer of crude oil, and Iran is a vital cog in that wheel. Losing access to Iranian oil would not only jeopardize China’s energy security but could also lead to rising prices and economic instability.
Iran, in turn, supplies 13% of China’s total crude imports.
Now, let’s flip the coin. Iran needs China just as much as China needs Iran. As per Bloomberg, Iran supplies around 13% of China’s total crude imports. This relationship is mutually beneficial, but it also creates a delicate balance. If the U.S. were to increase its presence in Iran, it could disrupt this lucrative partnership, forcing China to seek alternatives that might not be as favorable.
Disruption means China…
Disruption of oil supplies doesn’t just mean a spike in prices at the pump; it means potential instability and uncertainty in markets that have become accustomed to this flow. For China, which prioritizes economic stability, any hint of disruption could trigger a domino effect, impacting everything from manufacturing to consumer spending.
Moreover, the geopolitical implications of U.S. interference in Iran could lead to an escalation of tensions not just between the U.S. and Iran, but also between the U.S. and China. It’s a high-stakes game, with each country maneuvering to protect its interests while navigating a complex web of alliances and rivalries.
China’s strategy in the Middle East
China’s approach to the Middle East is strategic and often understated. Unlike the U.S., which has historically employed military presence and intervention as a means of influence, China prefers economic partnerships and investments. This tactic has allowed China to build strong ties with multiple countries in the region, positioning itself as a critical player in the energy market.
Through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China is investing heavily in infrastructure and energy projects across the Middle East, including Iran. This not only secures access to vital resources but also strengthens economic ties that can be leveraged in political negotiations. The Belt and Road Initiative is a testament to China’s long-term strategy of establishing itself as a dominant force in global trade and energy supply.
The U.S. response and its implications
The United States, on the other hand, has a different approach. Historically, it has sought to contain Iran through sanctions and military presence. This policy has often led to heightened tensions not just with Iran but also with China, who views U.S. actions as a threat to its energy security and economic interests. The U.S. aims to limit Iran’s influence in the region, believing that a strong Iran could challenge American interests and allies.
As tensions continue to rise, particularly with the ongoing discussions about Iran’s nuclear program, the U.S. might see any increase in its presence as a way to counteract Chinese influence. However, this could backfire. Increased U.S. presence in Iran doesn’t just threaten Iran; it also threatens the energy supplies that China relies on. As noted by Foreign Policy, any disruption could lead to a ripple effect that impacts global oil markets.
Looking ahead: The future of U.S.-China-Iran relations
As we look ahead, the relationship between these three nations will be critical to monitor. The stakes are high, with energy needs, economic stability, and geopolitical power all hanging in the balance. If the U.S. continues its current trajectory, we could see an increase in hostilities that may not only affect Iran and China but also have broader implications for global oil markets and international relations.
In this tangled web of international relations, one thing is clear: China will do whatever it takes to secure its energy needs and maintain its economic growth. And keeping the U.S. out of Iran is a crucial part of that strategy. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone interested in global politics, economics, or energy security.
Final thoughts
In a world where energy is power, the relationship between China, Iran, and the U.S. will continue to evolve. The interplay between these nations will be a key factor in shaping not just regional stability but also global energy markets. As we watch this unfold, it becomes increasingly important to consider the implications of these relationships for our own economies and lives.
So next time you hear about tensions in Iran or discussions of U.S. foreign policy, remember the underlying factors at play: oil, economics, and the quest for power. Understanding these connections can provide a clearer picture of why nations act the way they do on the global stage.
