“Shocking Discovery: What Your Hematuria Reveals About Your Health Risks!”
hematuria symptoms, urinary tract infection causes, kidney health awareness 2025
—————–
Understanding Hematuria: Causes, Symptoms, and Implications
Hematuria, the presence of blood in urine, can be a concerning symptom that indicates various underlying health issues. It is essential to understand the potential causes of hematuria, its symptoms, and when to seek medical attention.
What is Hematuria?
Hematuria is classified into two types: gross hematuria, where blood is visible to the naked eye, and microscopic hematuria, which can only be detected through laboratory tests. This condition can occur for a variety of reasons, primarily due to issues with the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract.
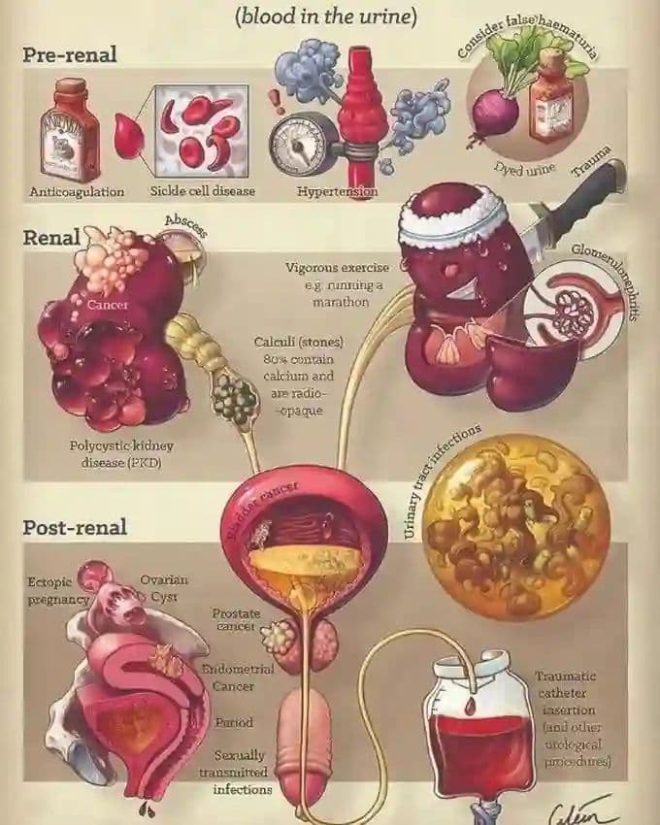
Causes of Hematuria
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are one of the most common causes of hematuria, particularly in women. They can lead to inflammation and irritation of the bladder and urethra, resulting in blood being present in the urine. - Kidney Stones
The formation of stones in the kidneys can cause significant pain and bleeding as they move through the urinary tract. The sharp edges of the stones can damage the lining of the urinary tract, leading to hematuria. - Glomerulonephritis
This is an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units, which can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or other conditions. Glomerulonephritis can lead to both hematuria and proteinuria (excess protein in urine). - Trauma or Injury
Physical injuries to the kidneys or bladder can cause bleeding. Sports injuries or accidents can result in hematuria due to damage to these organs. - Cancer
Hematuria can be a sign of bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer. In these cases, blood in the urine is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain or difficulty urinating. - Enlarged Prostate
In men, an enlarged prostate can lead to hematuria. The enlarged tissue can compress the urethra, leading to urinary problems and bleeding. - Inherited Disorders
Conditions like sickle cell anemia or Alport syndrome can also result in hematuria due to their impact on kidney function and blood vessels. - Medications
Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the risk of bleeding and may contribute to hematuria. - Vascular Disorders
Conditions affecting blood vessels, such as vasculitis, can lead to inflammation and bleeding in the urinary tract.Symptoms Accompanying Hematuria
While the primary symptom of hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine, other symptoms may accompany this condition depending on the underlying cause. These can include:
- Pain during urination
- Frequent urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever and chills (in cases of infection)
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you notice blood in your urine, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, fever, or changes in urination habits. A healthcare provider can perform diagnostic tests, including urinalysis, imaging studies, and possibly cystoscopy, to determine the underlying cause of hematuria.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing hematuria involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, along with laboratory tests to assess kidney function and check for infections or abnormalities in the urine. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment options will vary:
- UTI: Typically treated with antibiotics.
- Kidney Stones: Management may involve hydration, pain relief, or procedures to remove or break down stones.
- Glomerulonephritis: Treatment may include medications to reduce inflammation and control blood pressure.
- Cancer: May require surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
- Prostate Issues: Treatments can range from medication to surgical interventions.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of hematuria can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of urinary tract issues. Staying well-hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding known irritants can support urinary health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also aid in early detection and management of potential issues.
Conclusion
Hematuria is a symptom that can indicate a range of underlying health conditions, from benign to serious. Understanding its causes and symptoms is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. If you experience blood in your urine, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate management. Taking proactive steps towards urinary health can help mitigate risks and promote overall well-being.
The cause of hematuria
This condition occurs when the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract allow blood cells to leak into the urine. https://t.co/lare2dfN6G

The cause of hematuria
Hematuria is a medical term that might sound a bit scary, but let’s break it down together. Essentially, hematuria occurs when there are blood cells in your urine. It’s a condition that can be caused by various factors affecting the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. If you’ve noticed that your urine looks reddish or brownish, it’s definitely something to pay attention to. In this article, we’ll explore the different causes of hematuria, what symptoms to watch for, and when to seek medical help.
This condition occurs when the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract allow blood cells to leak into the urine.
So, what exactly leads to this blood leakage? Hematuria can be classified into two types: gross and microscopic. Gross hematuria is when you can see the blood in your urine with the naked eye, while microscopic hematuria is when blood is only detectable under a microscope. Both types are important and can indicate underlying health issues.
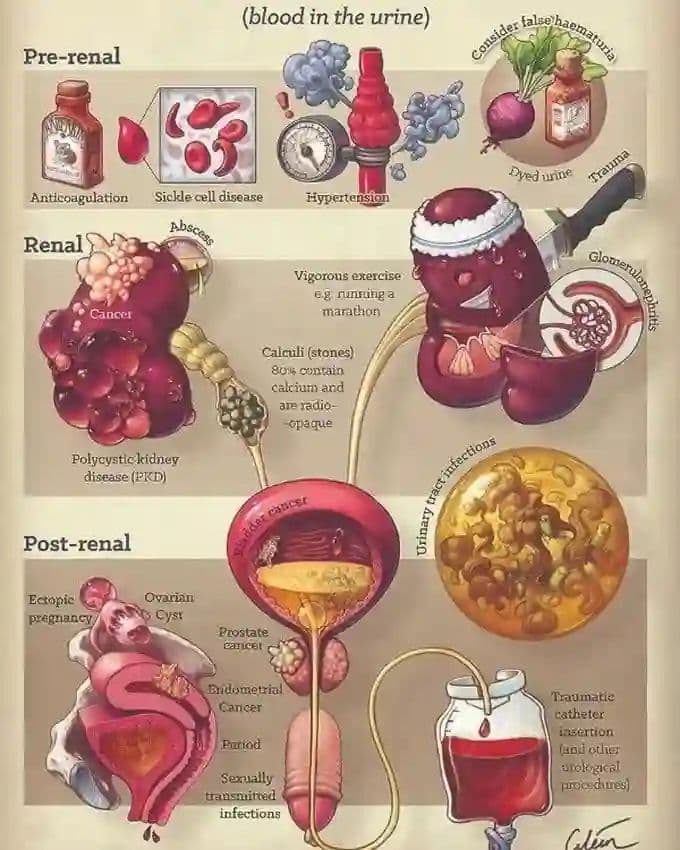
There are numerous causes of hematuria, ranging from benign to serious conditions. Some common causes include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and trauma. Let’s take a closer look at these causes.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
One of the most common culprits behind hematuria is urinary tract infections. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing inflammation and infection. Symptoms of a UTI often include frequent urination, a burning sensation while urinating, and cloudy urine. In some cases, blood may be present as well. If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for appropriate treatment, usually involving antibiotics. You can learn more about UTIs and their symptoms on the [Mayo Clinic website](https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-tract-infection/symptoms-causes/syc-20353087).
Kidney Stones
Another common cause of hematuria is kidney stones. These hard deposits form in your kidneys, and as they move through your urinary tract, they can cause significant pain and bleeding. If you’ve ever experienced the sharp, excruciating pain associated with kidney stones, you know just how uncomfortable they can be. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and pain that radiates to the lower abdomen or groin. If you suspect kidney stones, it’s best to seek medical advice for diagnosis and treatment options, which can range from increased hydration to surgical intervention. Check out the [Cleveland Clinic](https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10204-kidney-stones) for more information on kidney stones.
Trauma or Injury
Trauma or injury to the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract can also lead to hematuria. This could be from a sports injury, an accident, or even a fall. If you’ve experienced a significant impact to your abdomen or lower back, and you notice blood in your urine, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Injuries can lead to complications that require immediate care. You can read more about the effects of trauma on the body by visiting [WebMD](https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/injuries).
Other Medical Conditions
Apart from UTIs and kidney stones, several other medical conditions can cause hematuria. For instance, glomerulonephritis, which is an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units, can lead to blood in the urine. Additionally, conditions like polycystic kidney disease and certain cancers (bladder cancer, kidney cancer) are also potential causes. If you have a family history of these conditions or are experiencing other concerning symptoms, a healthcare professional should evaluate your situation.
Medications and Blood Disorders
Certain medications may also contribute to hematuria. For example, blood thinners like warfarin or aspirin can increase your risk of bleeding, which may manifest as blood in your urine. Moreover, blood disorders such as hemophilia can lead to abnormal bleeding patterns, including hematuria. If you are on medication or have a blood disorder, it’s essential to discuss any symptoms with your healthcare provider.
Symptoms Accompanying Hematuria
While blood in your urine is the primary symptom of hematuria, it often comes with other symptoms depending on the underlying cause. You might experience pain in your side or back, frequent urination, or burning sensations while urinating. If hematuria is due to a kidney stone, you may also have severe pain that comes in waves. It’s important to keep an eye on these accompanying symptoms as they can provide clues to what’s going on in your body.
When to See a Doctor
It’s vital to know when to seek medical attention for hematuria. If you notice blood in your urine, especially if it’s accompanied by pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment can make all the difference. Even if you don’t have additional symptoms, it’s still a good idea to get hematuria evaluated, as it may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Diagnosis of Hematuria
When you visit a doctor with concerns about hematuria, they will likely start with a thorough medical history and physical examination. You may undergo tests like urinalysis, blood tests, imaging studies (like an ultrasound or CT scan), or even a cystoscopy, where a thin tube is inserted into your bladder to look for abnormalities. These tests help pinpoint the exact cause of hematuria so that appropriate treatment can be administered.
Treatment Options
The treatment for hematuria largely depends on its underlying cause. For UTIs, antibiotics are commonly prescribed. Kidney stones might require increased fluid intake, medication, or in some cases, surgery. If a more serious condition is identified, such as cancer, your treatment plan will be tailored to your specific diagnosis. This could involve anything from surgery to chemotherapy.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of hematuria can be prevented, there are some measures you can take to reduce your risk. Staying hydrated is crucial; drinking plenty of water helps flush out your urinary system and may prevent infections and stones. Practicing good hygiene, especially for women, can also help prevent UTIs. If you have a family history of kidney issues or other related conditions, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help catch any problems early.
In summary, hematuria can be a concerning condition, but understanding its causes and symptoms can empower you to take action. Whether it’s a minor issue like a UTI or something more serious, seeking medical advice is essential. Remember, your health is in your hands, and being proactive is key! Always listen to your body, and don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns.
This condition occurs when the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract allow blood cells to leak into the urine.
