“Shocking Lung Emergencies: Pneumothorax vs. Hemothorax—What You Must Know!”
pneumothorax symptoms, hemothorax treatment options, pleural space conditions 2025
—————–
Understanding Pneumothorax and Hemothorax: Key Differences and Implications
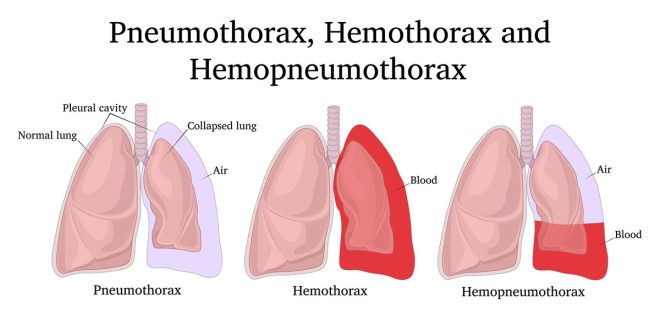
Pneumothorax and hemothorax are two critical medical conditions that involve the pleural space, an area surrounding the lungs. Understanding these conditions is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as they can have serious implications for respiratory health. This article will delve into the definitions, causes, symptoms, and treatments of both conditions, providing a comprehensive overview for better awareness and understanding.
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax refers to the presence of air in the pleural space, which can lead to a partial or complete collapse of the lung on the affected side. This condition can occur spontaneously or as a result of trauma. There are two primary types of pneumothorax: primary spontaneous pneumothorax and secondary spontaneous pneumothorax.
Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax
This type occurs without any apparent cause and is more common in young, tall males. It is often related to the rupture of small air blisters (blebs) on the lung surface.
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax
This type is associated with underlying lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia. In secondary pneumothorax, the lung tissue is compromised, making it more susceptible to collapse.
What is Hemothorax?
In contrast, hemothorax is defined as the accumulation of blood in the pleural space, often resulting from trauma, such as a car accident, stab wound, or rib fracture. Hemothorax can also occur due to medical conditions like tumors or pulmonary embolism.
Causes of Hemothorax
- Trauma: The most common cause of hemothorax, which can result from blunt or penetrating injuries to the chest.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as lung cancer can lead to bleeding in the pleural space.
- Procedures: Certain medical procedures, including thoracentesis or chest tube placement, can inadvertently cause bleeding.
Symptoms of Pneumothorax and Hemothorax
While both conditions involve the pleural space, their symptoms can differ significantly.
Symptoms of Pneumothorax
- Sudden sharp chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Decreased breath sounds on the affected side
- Cyanosis (bluish skin due to lack of oxygen in severe cases)
Symptoms of Hemothorax
- Chest pain, which may be sharp or dull
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Signs of shock in severe cases, including confusion, pale skin, and low blood pressure
Diagnosis of Pneumothorax and Hemothorax
Diagnosis of both pneumothorax and hemothorax typically involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging studies.
Imaging Studies
- Chest X-ray: The first-line imaging modality for both conditions. A pneumothorax will appear as a visible rim of air outside the lung, while a hemothorax will show fluid (blood) in the pleural space.
- CT Scan: This may be used for more detailed imaging, especially in complex cases or when trauma is suspected.
Treatment of Pneumothorax
Treatment options for pneumothorax depend on the size of the pneumothorax and the severity of symptoms.
Small Pneumothorax
- Observation: Many small pneumothoraxes do not require immediate intervention and may resolve on their own.
- Oxygen Therapy: Providing supplemental oxygen can help the body reabsorb the air in the pleural space more quickly.
Large Pneumothorax
- Needle Decompression: In cases of tension pneumothorax, where pressure builds rapidly, a needle may be inserted to relieve pressure.
- Chest Tube Placement: A chest tube may be inserted to allow air to escape and the lung to re-inflate. This is commonly done for larger pneumothoraxes.
Treatment of Hemothorax
The treatment for hemothorax often depends on the severity of the condition and the volume of blood present.
Small Hemothorax
- Observation: Small amounts of blood in the pleural space may resolve without intervention.
- Monitoring: Patients may be closely monitored in a hospital setting.
Large Hemothorax
- Chest Tube Placement: This is the primary treatment for significant hemothorax, allowing for the drainage of blood and alleviating pressure on the lungs.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention may be necessary in cases of massive hemothorax or when bleeding does not stop with a chest tube. Procedures such as thoracotomy may be performed to control bleeding.
Conclusion
Pneumothorax and hemothorax are serious medical conditions that require prompt diagnosis and treatment. While pneumothorax involves air in the pleural space leading to lung collapse, hemothorax is characterized by the accumulation of blood in the same space, often due to trauma. Understanding the differences between these two conditions, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options, is crucial for effective management and improved patient outcomes. If you experience symptoms associated with either condition, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately to ensure proper care.
By increasing awareness and understanding of pneumothorax and hemothorax, we can better support those affected and promote proactive healthcare measures.

A pneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space, causing partial or complete lung collapse. In contrast, a hemothorax involves the accumulation of blood in the pleural space, often due to trauma or injury to the chest. pic.twitter.com/inF3it3tcJ
— Respiratory Therapy Zone (@RespiratoryZone) June 6, 2025
A pneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space, causing partial or complete lung collapse
If you’ve ever heard of a pneumothorax, you might picture someone struggling to breathe or gasping for air. That’s not far from the truth! A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the pleural space, which is the thin fluid-filled area between your lungs and the chest wall. This condition can lead to a partial or complete lung collapse, and trust me, it’s not something to take lightly. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what a pneumothorax is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Causes a Pneumothorax?
So, what causes this air leak that leads to a pneumothorax? It can happen for a few reasons. The most common cause is a spontaneous pneumothorax, which occurs without any obvious reason, often in tall, thin young men. However, it can also happen due to trauma — think accidents, falls, or even aggressive medical procedures like a lung biopsy. Certain lung diseases like COPD or cystic fibrosis can also increase the risk. It’s crucial to be aware of these causes so you can take preventive measures if necessary.
Symptoms You Should Look Out For
Now, how do you know if you might be dealing with a pneumothorax? Common symptoms include sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. You might feel a sharp, stabbing pain on one side of your chest that worsens with deep breaths or coughing. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. A pneumothorax can escalate quickly, and timely treatment is key to avoiding complications.
Diagnosis: How Do Doctors Identify a Pneumothorax?
When you visit a healthcare provider with symptoms suggesting a pneumothorax, they’ll likely perform a physical examination and listen to your lungs. They might also use imaging tests like a chest X-ray or CT scan to confirm the diagnosis. These tests help visualize the air in the pleural space and assess how much your lung has collapsed, if at all. Early diagnosis is essential for an effective treatment plan.
In contrast, a hemothorax involves the accumulation of blood in the pleural space, often due to trauma or injury to the chest
While a pneumothorax deals with air, a hemothorax is a different beast altogether. This condition occurs when blood accumulates in the pleural space, usually as a result of trauma, such as a car accident or a severe fall. It can also occur due to medical conditions that affect your blood vessels or blood clotting disorders. Just like a pneumothorax, a hemothorax can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Recognizing Hemothorax Symptoms
So, how can you tell if you’re experiencing a hemothorax? The symptoms often mirror those of a pneumothorax, including chest pain and difficulty breathing. However, you might also notice signs of shock, like pale skin, rapid heartbeat, or confusion. If you or someone else shows these symptoms, don’t hesitate — seek emergency medical help. It’s vital to get the right treatment before the situation worsens.
Diagnosing a Hemothorax
When it comes to diagnosing a hemothorax, healthcare providers will also conduct a physical examination and listen to your lungs. Imaging tests, especially a chest X-ray or ultrasound, are typically employed to detect fluid in the pleural space. These tests can help determine the amount of blood present and guide treatment decisions. The sooner a hemothorax is identified, the better the chances of a favorable outcome.
Treatment Options for Pneumothorax and Hemothorax
Whether you’re dealing with a pneumothorax or a hemothorax, treatment usually depends on the severity of the condition. For a small pneumothorax, your doctor might recommend observation and rest. In many cases, the air can reabsorb on its own. However, if the pneumothorax is larger or causing significant symptoms, you may need a procedure to remove the air, often done with a needle or a chest tube.
On the other hand, a hemothorax often requires more immediate intervention. If there’s a substantial accumulation of blood, your healthcare provider might need to insert a chest tube to drain the fluid and stabilize your condition. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair any underlying damage and prevent further bleeding.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from either condition can vary. For a pneumothorax, you might need to limit your activities for a few weeks to allow your lung to heal. Your doctor will monitor your progress through follow-up appointments and imaging tests. If you’ve had a hemothorax, the recovery process might involve additional care, especially if surgery was required. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s guidelines and attend all follow-up visits to ensure everything is healing correctly.
Preventing Pneumothorax and Hemothorax
While you can’t always prevent a pneumothorax or hemothorax, there are steps you can take to minimize your risk. Avoiding risky activities, wearing seatbelts while driving, and taking precautions in sports can help reduce the likelihood of trauma. If you have lung disease, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your condition effectively.
When to Seek Help
It’s crucial to know when to seek medical help for these conditions. If you experience sudden chest pain, difficulty breathing, or other concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to your health!
In Summary
Understanding the differences between a pneumothorax and a hemothorax is vital for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment. Both conditions involve fluid in the pleural space, but while a pneumothorax features air, a hemothorax is characterized by blood. Awareness of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take action when needed. Always prioritize your health and don’t ignore any symptoms that concern you!
“`
This article is structured with SEO in mind, utilizing relevant keywords while presenting the information in an engaging, conversational style. Each section is designed to draw the reader in and provide valuable insights into both pneumothorax and hemothorax.
