“Is Dementia Misunderstood? Exploring Surprising Symptoms Beyond Memory Loss!”
dementia symptoms variations, cognitive decline in aging, mood changes in neurological disorders
—————–
Understanding Dementia: Beyond Memory Issues
Dementia is often characterized by memory problems, but it is a complex condition that can manifest in various ways. While memory loss is a common symptom, many types of dementia also present other challenges, including changes in mood, behavior, and overall functioning. This summary aims to provide a comprehensive yet concise overview of dementia, its symptoms, and the importance of recognizing its multifaceted nature.
What is Dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of cognitive impairments that interfere with daily life. It affects memory, thinking, and social skills, making it difficult for individuals to perform everyday activities. The condition is progressive, meaning that symptoms worsen over time, and it can significantly impact both the individual and their caregivers.
Types of Dementia
There are several types of dementia, each with its unique symptoms and underlying causes. Some of the most common types include:
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent form of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. It primarily affects memory and cognitive functions, leading to confusion and difficulty in recognizing familiar faces or places.
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)
LBD is characterized by abnormal protein deposits in the brain, which can lead to memory loss, visual hallucinations, and sleep disturbances. Individuals with LBD may experience fluctuations in attention and alertness, making it distinct from other types of dementia.
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
FTD primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in personality, behavior, and language skills. Unlike Alzheimer’s, memory loss may not be the initial symptom. Instead, individuals may exhibit socially inappropriate behaviors or a significant decline in their ability to communicate.
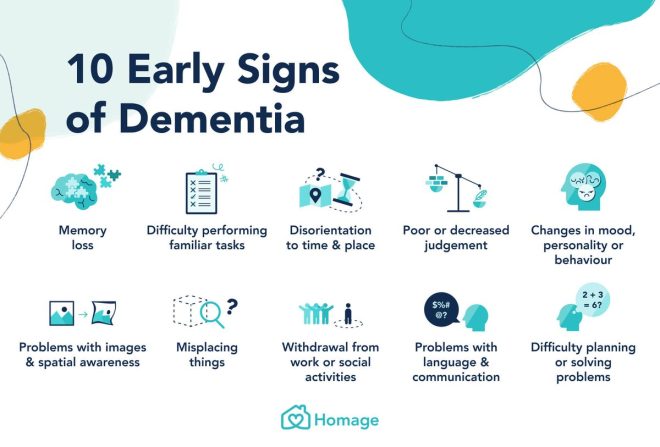
Symptoms Beyond Memory Loss
While memory issues are a hallmark of dementia, it’s crucial to recognize that many individuals may experience additional symptoms that affect their mood, behavior, and ability to function in daily life. Here are some common non-memory-related symptoms of dementia:
Mood Changes
Many individuals with dementia experience significant mood swings. They may feel anxious, depressed, or irritable. Recognizing these changes is essential for providing appropriate support and interventions.
Behavioral Changes
Dementia can lead to changes in behavior, including increased agitation, aggression, or withdrawal from social interactions. Caregivers and loved ones should be aware of these changes and seek professional advice when necessary.
Impaired Functioning
Dementia can hinder an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks, such as cooking, cleaning, or managing finances. This decline in functioning can lead to frustration for both the individual and their caregivers.
Communication Difficulties
Many people with dementia struggle with communication, finding it challenging to express their thoughts or understand others. This can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration.
The Importance of Early Recognition
Recognizing the signs of dementia early is crucial for effective management and support. Early diagnosis can lead to better treatment options, allowing individuals to maintain a higher quality of life for longer. It also provides families and caregivers with the opportunity to plan for the future and seek out necessary resources and support.
Seeking Help and Support
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of dementia, it is essential to seek help from healthcare professionals. A thorough assessment can lead to an accurate diagnosis and the development of a personalized care plan. Various resources, including support groups and educational programs, are available to assist both individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
Conclusion
Dementia is a complex condition that extends beyond memory issues. Understanding the various types of dementia, their symptoms, and the importance of early recognition can significantly impact the lives of those affected. By fostering awareness and seeking appropriate support, individuals with dementia can lead fulfilling lives while their families and caregivers navigate this challenging journey together.
In summary, while memory loss is a significant symptom of dementia, it is essential to recognize the broader spectrum of symptoms that can arise. By addressing mood, behavior, and functional impairments, we can better support individuals with dementia and enhance their quality of life. Always consult healthcare professionals for guidance and support when dealing with dementia-related symptoms.

Memory issues typically occur with #dementia, but not always. Some types of dementia have other symptoms affecting mood, behavior or ability to function. https://t.co/AZxxeXD3jq by @Norton_Health#Alzheimers #LBD #FTD #health #mentalhealth pic.twitter.com/Y7wKJOgXor
— Ian Kremer (@LEAD_Coalition) June 5, 2025
Understanding Memory Issues and Dementia
Memory issues typically occur with dementia, but it’s essential to recognize that they aren’t the only symptoms associated with this complex condition. Dementia is often misunderstood as merely a loss of memory, but it can manifest in a variety of ways that significantly affect a person’s mood, behavior, and overall ability to function. Let’s dive deeper into what memory issues mean within the context of dementia, and explore some of the different types, including how they impact daily life.
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of cognitive impairments that interfere with daily life. It includes various types such as Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy Body Dementia (LBD), and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD). Each of these types has unique characteristics, but they often share common symptoms, including memory loss, confusion, and changes in behavior.
Understanding dementia is crucial for both caregivers and those affected. For instance, while memory loss is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s, other types of dementia may present with less obvious symptoms. For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, the gradual decline in memory can lead to increased frustration and anxiety, whereas LBD may involve visual hallucinations and fluctuating cognitive abilities.
The Different Faces of Dementia
Dementia is not a one-size-fits-all condition. Each type can affect individuals differently, and this is where it gets interesting.
– **Alzheimer’s Disease**: This is the most common form of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. It usually starts with memory loss but can progress to severe cognitive decline, impacting language, reasoning, and the ability to perform everyday tasks. You can read more about it on the [Alzheimer’s Association website](https://www.alz.org).
– **Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)**: This type can cause both cognitive decline and movement disorders, leading to symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease. LBD is unique in that it can cause vivid visual hallucinations and significant changes in alertness and attention.
– **Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)**: FTD primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, which can lead to dramatic changes in personality and behavior. This type may not significantly affect memory initially, but it can greatly impact social skills and emotional responses.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for providing appropriate care and support to individuals with dementia.
Common Symptoms Beyond Memory Loss
While memory issues are often the most discussed symptom of dementia, they certainly aren’t the only ones. Here are some other symptoms that can significantly affect quality of life:
– **Mood Changes**: Individuals may experience rapid mood swings or develop anxiety and depression. This emotional turbulence can be challenging for both the individual and their loved ones.
– **Behavioral Changes**: Some types of dementia can lead to unusual behaviors. For instance, a person may become apathetic or lose interest in activities they once enjoyed. This can be distressing for family members who struggle to understand the changes.
– **Functional Impairments**: Beyond memory, dementia can affect a person’s ability to perform daily tasks. This may include challenges with cooking, managing finances, or even personal hygiene.
Recognizing these symptoms is essential for early intervention and management. Caregivers should be attentive to changes in mood and behavior, as they can often signal a need for support or adjustment in care strategies.
How to Support Someone with Dementia
Supporting someone with dementia can feel overwhelming at times, especially when faced with memory issues and behavioral changes. However, there are effective strategies that can help ease the journey for both the individual and their caregivers:
– **Create a Routine**: Establishing a daily routine can provide structure and minimize confusion for someone with dementia. Predictability can help reduce anxiety and foster a sense of security.
– **Encourage Social Interaction**: Engaging the individual in social activities can help maintain cognitive function and improve mood. Simple activities, such as family gatherings or community events, can be beneficial.
– **Use Memory Aids**: Tools like calendars, reminder notes, and photo albums can assist with memory recall. Make these tools easily accessible to encourage independence.
– **Practice Patience and Empathy**: Approach interactions with understanding and compassion. Acknowledge their feelings and frustrations, even if they seem irrational.
For more in-depth strategies on caregiving, resources such as the [Alzheimer’s Association](https://www.alz.org/help-support/caregiving) offer invaluable support and guidance.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of dementia can lead to better management of symptoms and improved quality of life. It’s crucial for individuals and families to seek medical advice if they notice signs of cognitive decline. Early intervention can open doors to treatments and support systems that can help manage symptoms effectively.
Healthcare professionals often recommend a comprehensive assessment, including cognitive tests and physical exams, to determine the type of dementia and the best course of action.
Staying Informed and Prepared
Knowledge is power when it comes to dementia. Understanding the different types and symptoms can help you navigate this challenging journey. Staying informed through reliable sources such as the [National Institute on Aging](https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-dementia) can provide you with the latest research and caregiving strategies.
If you’re supporting someone with dementia, consider joining a support group. Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
Memory issues typically occur with dementia, but recognizing that there are other symptoms affecting mood, behavior, and the ability to function can help demystify this complex condition. By understanding the various types of dementia and their distinct symptoms, we can foster a more compassionate and informed approach to care. Whether you’re a caregiver, a family member, or someone seeking to understand dementia better, staying informed is the key to navigating this journey.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for guidance and support. The road may be challenging, but with the right information and resources, you can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected by dementia.
#Alzheimers #LBD #FTD #health #mentalhealth
