Understanding Propaganda: A Deep Dive into Communication Tactics
Introduction
In the digital age, the term "propaganda" often surfaces in discussions about media influence and political rhetoric. Defined as "the spreading of ideas, information, or rumor for the purpose of helping or injuring an institution, a cause, or a person," propaganda plays a crucial role in shaping public perception and opinion. This summary will explore the nuances of propaganda, how it operates in contemporary society, and the implications of its use, particularly in political contexts.
What is Propaganda?
Propaganda is a deliberate form of communication aimed at influencing the attitudes and behaviors of individuals towards a particular cause or viewpoint. It can take many forms, including advertisements, news articles, social media posts, and more. The essence of propaganda lies in its strategic intent, whether to promote a positive image or to discredit an opponent.
The Mechanisms of Propaganda
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
- Selective Information Dissemination: One of the primary tactics of propaganda is the selective release of information. By presenting only certain facts or viewpoints, propagandists can craft a narrative that supports their agenda while ignoring opposing perspectives.
- Emotional Appeal: Propaganda often relies on emotional triggers to elicit responses from the audience. By appealing to fear, pride, or anger, propagandists can motivate individuals to act in favor of or against a particular cause.
- Repetition: The use of repetitive messaging reinforces ideas and makes them more memorable. When the same message is encountered multiple times, it can create a sense of familiarity and acceptance among the audience.
- Symbolism and Imagery: Visual elements, such as logos, colors, and slogans, play a significant role in propaganda. These symbols can evoke strong emotions and associations, making the message more impactful.
The Role of Social Media in Propaganda
In recent years, social media platforms have become powerful tools for the spread of propaganda. The ability to share information quickly and widely allows for rapid dissemination of ideas, sometimes without verification. This has led to the rise of misinformation and disinformation campaigns that can sway public opinion and influence political outcomes.
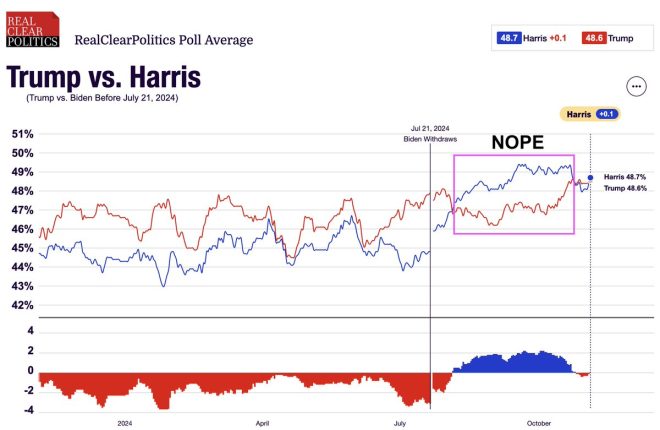
For example, the tweet from Rasmussen Reports highlights a critical moment in political discourse, where propaganda is used to shape narratives around candidates and their perceived standings. The assertion that "Harris was never ahead" suggests a deliberate attempt to undermine a political figure’s credibility, illustrating how propaganda can serve specific agendas.
The Consequences of Propaganda
The use of propaganda can have far-reaching consequences, both positive and negative. On one hand, it can mobilize support for important social issues and drive grassroots movements. On the other hand, it can also lead to division, polarization, and the erosion of trust in institutions and individuals.
Polarization and Division
Propaganda can exacerbate societal divides by presenting issues in black-and-white terms. When complex topics are oversimplified, it can lead to a lack of understanding and empathy among different groups. This polarization can manifest in hostile rhetoric and conflict, undermining democratic discourse.
Erosion of Trust
The pervasive nature of propaganda can also damage public trust in the media and political institutions. When individuals are bombarded with conflicting messages and misinformation, it becomes increasingly challenging to discern fact from fiction. This skepticism can lead to disengagement from the political process and a decline in civic participation.
Recognizing Propaganda
To navigate the complex landscape of information today, it is essential for individuals to develop critical thinking skills and media literacy. Here are some strategies to recognize and combat propaganda:
- Verify Sources: Always check the credibility of the source before accepting information as truth. Look for reputable organizations, fact-checking websites, and expert opinions.
- Analyze the Message: Consider the intent behind the message. Ask yourself who benefits from the information being presented and whether it presents a balanced view.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Expose yourself to a variety of viewpoints to gain a more comprehensive understanding of an issue. This can help counteract the effects of selective information dissemination.
- Engage in Open Dialogue: Foster discussions with individuals who hold different opinions. This can promote understanding and reduce polarization.
Conclusion
Propaganda is a powerful tool that can shape public opinion and influence political landscapes. Understanding its mechanisms and implications is crucial in today’s information-saturated society. By recognizing propaganda and developing critical thinking skills, individuals can better navigate the complexities of communication and contribute to a more informed and engaged citizenry.
In summary, while propaganda can serve various purposes, its potential for misuse necessitates vigilance and discernment. The ongoing dialogue about its role in politics and society underscores the importance of transparency, accountability, and education in fostering a healthy democratic process. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too must our approaches to understanding and combating propaganda.

propaganda – noun – prŏp″ə-găn′də – the spreading of ideas, information, or rumor for the purpose of helping or injuring an institution, a cause, or a person
STILL no explanations – no apologies – no comments
Harris was never ahead, they knew it, and they did this https://t.co/5fGwMY5yan pic.twitter.com/MisYRFO4Aw
— Rasmussen Reports (@Rasmussen_Poll) May 4, 2025
Understanding Propaganda: A Deeper Dive
Propaganda is a term that often gets thrown around in political discussions, media critiques, and even casual conversations. But what does it really mean? According to the dictionary, propaganda is defined as “the spreading of ideas, information, or rumor for the purpose of helping or injuring an institution, a cause, or a person.” This definition captures the essence of how information can be manipulated to serve specific agendas, whether that be for good or ill.
The Role of Propaganda in Politics
Let’s face it—politics can be a dirty game. Politicians and their teams often use propaganda to sway public opinion, bolster support, or discredit opponents. This can take many forms, from misleading advertisements to selective reporting in the news. The recent tweet by Rasmussen Reports points to a situation where there were “STILL no explanations – no apologies – no comments” regarding a particular political stance. This lack of transparency can often fuel speculation and mistrust among the public.
Case Study: Kamala Harris
To better understand how propaganda operates, let’s examine the case of Kamala Harris. The tweet from Rasmussen suggests that “Harris was never ahead, they knew it, and they did this”, implying that certain narratives were pushed despite the reality of the situation. It raises questions about the integrity of political reporting and the intentions behind it. Was the media complicit in promoting a false narrative? How much of what we consume as news is influenced by propaganda techniques?
The Psychology Behind Propaganda
Understanding why propaganda works requires a look at human psychology. People are often driven by emotions rather than facts. When information is presented in a way that stirs up feelings—be it fear, hope, or anger—it tends to resonate more deeply. This emotional appeal is a powerful tool for those looking to persuade or manipulate public opinion. Think about it: how often do you find yourself swayed by a compelling story rather than sheer statistics?
Modern Examples of Propaganda
In today’s digital age, the spread of propaganda has taken on new forms. Social media platforms amplify messages at lightning speed, making it easier for misinformation to circulate. From viral memes to clickbait headlines, the landscape is rife with examples of propaganda in action. For instance, during elections, you might see targeted ads that use emotional triggers to sway undecided voters.
The Consequences of Propaganda
The ramifications of propaganda can be severe. When the public is bombarded with skewed information, it can lead to polarization, misinformation, and a general distrust in institutions. This was evident during recent elections, where many voters felt confused and misled by the narratives being pushed by various media outlets. The Brookings Institution highlights how social media can create echo chambers, reinforcing existing beliefs and further dividing society.
Identifying Propaganda
If you want to become a more informed consumer of information, learning to identify propaganda is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Check the Source: Is the information coming from a reputable outlet? Do they have a history of reliable reporting?
- Look for Evidence: Are claims backed up by data? Are there citations to credible studies or reports?
- Analyze the Language: Is the language emotionally charged? Does it aim to provoke a reaction rather than present facts?
The Importance of Critical Thinking
In a world saturated with information, developing critical thinking skills is more important than ever. Ask yourself questions about the materials you consume: Who benefits from this information? What is the intent behind it? By engaging with content critically, you can better navigate the complexities of propaganda and make more informed decisions.
How to Combat Propaganda
So, how can we push back against the tide of propaganda? It starts with education. By fostering media literacy in our communities, we can equip individuals with the tools they need to discern fact from fiction. Encouraging open discussions about the impact of propaganda can also help break down the barriers that misinformation creates.
The Future of Information
As technology continues to evolve, the methods of spreading propaganda will likely become even more sophisticated. Artificial intelligence, deepfakes, and advanced algorithms present new challenges in discerning truth from deception. Staying informed about these developments is vital for anyone looking to navigate the modern information landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding propaganda is essential for anyone who wants to engage critically with the world around them. From politics to media, the power of propaganda is undeniable. By sharpening our critical thinking skills and becoming more discerning consumers of information, we can better protect ourselves from manipulation and contribute to a more informed society.
“`
This article dives deep into the concept of propaganda, discussing its implications, examples, and how to identify and combat it in an engaging, conversational manner. Each section builds on the previous one, creating a comprehensive understanding of this complex topic.
Breaking News, Cause of death, Obituary, Today
