No Automaker Can Escape Tariffs Completely
In the complex landscape of the automotive industry, tariffs play a significant role in shaping the financial dynamics of vehicle manufacturers. The imposition of tariffs can impact pricing, supply chains, and ultimately, consumer choices. However, the exposure to these tariffs is not uniform across all automakers. A recent analysis reveals the varying degrees of tariff exposure based on the percentage of vehicles assembled in the United States. This summary delves into the findings, highlighting the stark contrasts between different automakers.
U.S. Assembly as a Shield Against Tariffs
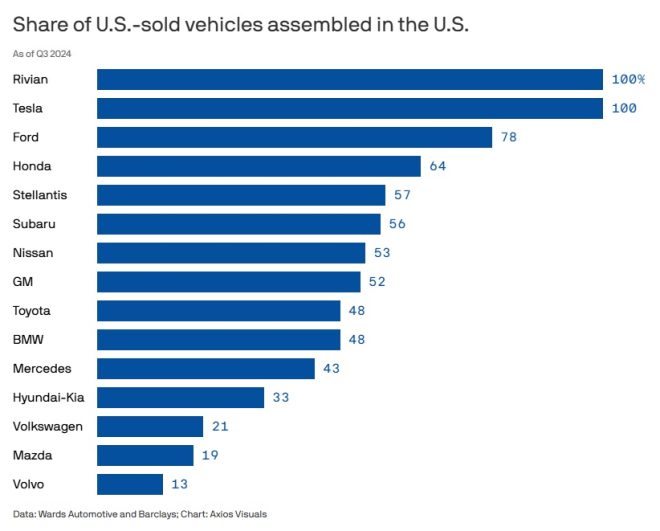
The ability of automakers to mitigate the impact of tariffs largely depends on their manufacturing locations. Vehicles assembled in the U.S. are less susceptible to tariffs, providing a competitive edge to companies like Tesla and Rivian, which boast an impressive 100% domestic assembly rate. This means that all their vehicles sold in the U.S. are manufactured within the country, allowing them to bypass additional costs associated with imported vehicles.
Ford follows closely with 78% of its vehicles assembled domestically. This substantial percentage indicates Ford’s commitment to local manufacturing, which not only helps the company avoid tariffs but also supports American jobs and the economy. The significance of local assembly cannot be overstated, as it serves as a buffer against external economic pressures that can arise from global trade policies.
The Other End of the Spectrum
Conversely, some automakers face considerable challenges due to their lower domestic assembly rates. For instance, Volvo, a well-known name in the automotive industry, has only 13% of its vehicles assembled in the United States. This limited domestic assembly exposes Volvo to higher tariff costs on its vehicles sold in the U.S. market, which could potentially affect pricing strategies and overall competitiveness.
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
The disparity in assembly rates underscores the varying levels of vulnerability among automakers. Manufacturers with a higher percentage of U.S.-assembled vehicles can leverage their domestic production to maintain more stable pricing and resist the upward pressure that tariffs can create. In contrast, companies with lower assembly rates may need to reevaluate their strategies to remain competitive in an increasingly tariff-sensitive market.
Strategic Implications for Automakers
As the landscape of tariffs and trade policies continues to evolve, automakers must adopt strategic approaches to navigate these challenges. Companies like Tesla and Rivian, with their commitment to domestic production, are well-positioned to capitalize on the current environment. Their ability to sell vehicles without the added burden of tariffs gives them a significant advantage over competitors with lower domestic assembly rates.
On the other hand, automakers like Volvo may need to reconsider their operational strategies to increase their local assembly footprint. By investing in U.S. production facilities, they can reduce their exposure to tariffs and enhance their competitiveness in the market. This could involve building new manufacturing plants or expanding existing ones to increase the percentage of vehicles assembled in the U.S.
Consumer Considerations
For consumers, the implications of these assembly rates and tariff exposures are significant. A higher percentage of U.S.-assembled vehicles typically translates to more favorable pricing and availability. Consumers may find that vehicles from automakers with a strong domestic presence offer better value compared to those with lower assembly rates. Additionally, supporting U.S. manufacturers can resonate with consumers who prioritize buying American-made products.
As consumers become increasingly aware of the impact of tariffs on vehicle pricing, they may seek out brands that demonstrate a commitment to local manufacturing. This shift in consumer behavior could further incentivize automakers to enhance their domestic production capabilities.
The Future of the Automotive Industry
The ongoing discussions surrounding tariffs and trade policies will undoubtedly continue to influence the automotive industry. As automakers assess their positions in the market, those with a proactive approach to domestic production are likely to thrive. The trend toward electrification and the rise of new entrants like Rivian and Tesla highlight the importance of innovation in addition to strategic manufacturing decisions.
In conclusion, while no automaker can escape tariffs entirely, the degree of exposure varies significantly based on the percentage of vehicles assembled in the United States. Companies like Tesla and Rivian lead the charge with 100% domestic assembly, followed by Ford at 78%. On the other end of the spectrum, Volvo’s 13% assembly rate exposes it to greater tariff-related challenges. As the automotive industry evolves, the balance between domestic production and global supply chains will remain a critical factor in determining competitiveness and consumer preferences. Automakers must adapt and innovate to navigate these challenges successfully, ultimately shaping the future of transportation in an increasingly interconnected world.

No automaker can escape tariffs completely:
But some are way less exposed.
Breaking down the share of U.S.-sold vehicles assembled in the U.S—Tesla and Rivian lead with 100% each, followed by Ford at 78%.
However—on the other end of the spectrum…
Volvo’s share is only 13%. https://t.co/wlipolmD5f
No automaker can escape tariffs completely:
In today’s global economy, tariffs have become a crucial topic of discussion, especially in the automotive industry. These tariffs can significantly impact manufacturers, influencing pricing, production, and ultimately, the consumer’s choice. But here’s the kicker—while no automaker can escape tariffs completely, some are way less exposed than others. Understanding how this plays out can help consumers make more informed decisions while also shedding light on the future landscape of the automotive market.
Breaking Down the Share of U.S.-Sold Vehicles Assembled in the U.S
Let’s dive into the numbers. When we break down the share of U.S.-sold vehicles that are assembled right here in the States, it becomes clear that there are some standout players. Tesla and Rivian lead the pack, boasting an impressive 100% assembly rate in the U.S. This means that every single vehicle they sell in the U.S. is also made in the U.S. That’s a huge advantage, particularly when it comes to navigating tariffs that might be imposed on imported vehicles.
Following closely is Ford, with 78% of its vehicles assembled domestically. This puts Ford in a strong position, as a significant portion of its sales are insulated from the fluctuations and uncertainties associated with tariffs. It’s clear that the more vehicles a company assembles in the U.S., the less exposure it has to tariff-related costs.
How Tariffs Affect Consumers and Automakers
Now, you might be wondering how this all impacts you as a consumer. When tariffs are imposed on imported vehicles, the costs often trickle down to the buyer. Increased tariffs can lead to higher vehicle prices, which means you might end up paying more for a car that’s made overseas. This is where companies like Tesla, Rivian, and Ford have a strategic advantage—they can keep their prices more stable and competitive because they have a larger share of vehicles assembled in the U.S.
On the flip side, manufacturers with a smaller domestic assembly percentage, like Volvo, which has only 13% of its U.S.-sold vehicles assembled in the U.S., face a higher risk. This risk translates to potential price increases and a more difficult sales environment. As consumers become more aware of these factors, they might gravitate towards brands that can offer more stability and assurance in pricing.
The Case of Volvo
Speaking of Volvo, their position is quite revealing. With only 13% of their vehicles assembled in the U.S., they have a much higher exposure to tariffs compared to their competitors. This raises questions about their pricing strategy and how they’ll adapt to a market that’s increasingly sensitive to tariffs. Are they going to absorb the costs, or will they pass them on to consumers? This uncertainty can create a hesitancy among potential buyers, impacting Volvo’s sales in the U.S. market.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
As consumers become more informed about the implications of tariffs, their preferences are likely to shift. The trend towards buying domestically assembled vehicles is not just a matter of national pride; it’s also a smart financial decision. With companies like Tesla and Rivian leading the charge with 100% domestic assembly, more buyers might find themselves inclined to support brands that keep jobs and manufacturing in the U.S.
Moreover, the current climate is pushing more automakers to rethink their strategies. Some might even consider relocating their manufacturing plants to the U.S. to mitigate tariff impacts. This could lead to a more competitive landscape where the consumer ultimately benefits from better prices and more choices.
Looking Ahead: The Future of the Automotive Industry
As we look to the future, it’s essential to keep an eye on how these dynamics evolve. The automotive industry is at a crossroads, with electric vehicles (EVs) gaining traction and traditional automakers adapting to a changing market. The ongoing discussions surrounding tariffs will undoubtedly shape the direction of this industry. Companies that can pivot quickly to meet consumer demands while managing tariff exposure will emerge as leaders.
It’s also worth mentioning the role of government policies in all of this. Tariffs can change based on political climates and negotiations. Staying informed about these changes can help consumers make better choices when purchasing a vehicle. The landscape can shift rapidly, and being ahead of the curve can offer significant advantages.
Final Thoughts on Tariffs and Automotive Choices
In conclusion, while no automaker can escape tariffs completely, the exposure varies significantly across brands. Tesla and Rivian stand out with their 100% U.S. assembly rate, while companies like Ford maintain a strong position with 78%. On the other end, Volvo’s 13% assembly rate poses challenges that could affect pricing and consumer perception.
As consumers, being aware of these factors allows us to make informed decisions about our vehicle purchases. The automotive landscape is changing, and understanding the implications of tariffs can help you choose a brand that aligns with your values and financial considerations. Whether you’re a loyal Ford fan or considering a Tesla for your next ride, knowing the assembly origin of your vehicle can empower you in your buying journey.
