Overview of U.S. Tariffs on Imports: A Detailed Breakdown
As of April 9, 2025, the United States implemented a series of significant tariffs on imports from various countries, marking a pivotal moment in international trade relations. This summary provides an in-depth analysis of the newly enacted tariffs, their implications, and the countries affected. Understanding these tariffs is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers, as they can influence market dynamics and economic trends.
What Are Tariffs?
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on imported goods. They are used to regulate trade between countries, protect domestic industries, and generate revenue for the government. Tariffs can lead to increased prices for consumers and can also affect the competitive landscape for businesses operating in the U.S. market.
Breakdown of Tariffs by Country
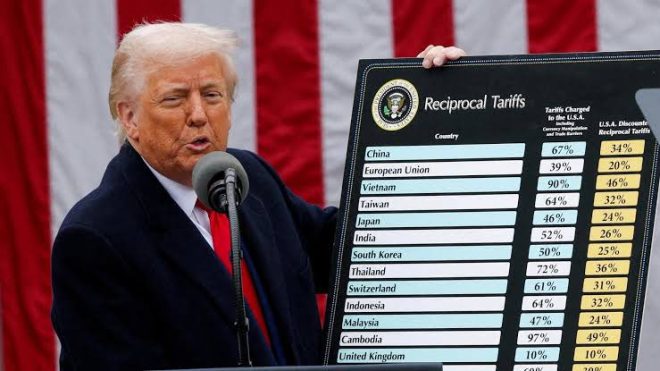
The recent announcement from the U.S. highlights various tariffs imposed on goods imported from specific countries. The highest tariff rates are as follows:
- China: 104%
- Lesotho: 50%
- Cambodia: 49%
- Laos: 48%
- Madagascar: 47%
- Vietnam: 46%
- Myanmar: 44%
- Sri Lanka: 44%
- Falkland Islands: 41%
- Syria: 41%
- Mauritius: 40%
- Iraq: 39%
- Guyana: 38%
These rates reflect the varying levels of trade tensions and economic strategies the U.S. government is employing against these nations.
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
The Implications of High Tariffs
Economic Impact
The introduction of high tariffs can have several economic implications:
- Increased Prices for Consumers: Consumers may face higher prices for imported goods due to the additional costs imposed by tariffs. This can lead to inflationary pressures within the economy.
- Shift in Supply Chains: Businesses may be forced to reevaluate their supply chains. Companies that rely heavily on imports from the affected countries may need to find alternative suppliers or consider domestic production options.
- Impact on Domestic Industries: While tariffs aim to protect domestic industries by making foreign goods more expensive, they can also lead to retaliatory measures from other countries, potentially harming U.S. exporters.
- Potential Trade Wars: High tariffs can escalate into trade disputes, leading to a tit-for-tat scenario where other countries impose their tariffs on U.S. goods, further complicating international trade relations.
Political Ramifications
The implementation of these tariffs is also laden with political significance. It reflects the U.S. government’s stance on trade and its approach to foreign policy. Tariffs can be used as a tool to exert pressure on other nations to change their trade practices or to address issues such as intellectual property theft or labor standards.
Country-Specific Considerations
Each country affected by the tariffs has unique economic ties to the U.S., and the impact of these tariffs will vary accordingly:
- China: As one of the largest trading partners of the U.S., the 104% tariff is a significant escalation in the long-standing trade tensions. This high tariff could lead to reduced imports from China, affecting various sectors, including technology and consumer goods.
- Vietnam and Cambodia: Both countries have seen increased trade with the U.S. in recent years. Tariffs of 46% and 49%, respectively, could disrupt the growing textile and manufacturing sectors in these nations.
- Countries like Lesotho and Madagascar: These nations may face severe economic challenges, as they often rely on U.S. markets for their exports. The 50% and 47% tariffs could lead to decreased demand for their products.
- Middle Eastern Nations: Tariffs on countries like Iraq and Syria could alter the dynamics of oil imports and other essential goods.
Conclusion
The implementation of high tariffs on imports from various countries represents a critical shift in U.S. trade policy. While the intention may be to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, the long-term effects on consumers, businesses, and international relations remain to be seen. As these tariffs take effect, stakeholders across the economic spectrum must stay informed and adapt to the evolving trade landscape.
This overview serves as a foundational understanding of the current state of U.S. tariffs, offering insights into their potential economic and political ramifications. As the global economy continues to navigate these changes, monitoring the impacts of these tariffs will be essential for predicting future trends in trade and commerce.

JUST IN: U.S. tariffs officially take effect:
China – 104%
Lesotho – 50%
Cambodia – 49%
Laos – 48%
Madagascar – 47%
Vietnam – 46%
Myanmar – 44%
Sri Lanka – 44%
Falkland Islands – 41%
Syria – 41%
Mauritius – 40%
Iraq – 39%
Guyana – 38%… pic.twitter.com/D7kUGczXXc— Suppressed news. (@SuppressedNws) April 9, 2025
JUST IN: U.S. tariffs officially take effect:
The world of international trade is buzzing with news about the latest tariffs imposed by the United States on various countries. If you’ve been paying attention, you know these tariffs have a significant impact on global markets and economies. In a move that has sent shockwaves through the trade community, the U.S. has officially rolled out new tariffs that range from a staggering 104% on China to 38% on Guyana. Let’s break down what this means for each of these countries and the global economy.
China – 104%
China faces the steepest tariff hike at 104%. This high tariff is part of a broader strategy to address trade imbalances and intellectual property concerns. The implications are massive. For U.S. consumers, this could mean higher prices on a wide range of products, from electronics to clothing. Importers will have to deal with increased costs, and many analysts fear that this could lead to retaliatory measures from China, further complicating trade relations.
The U.S. has long had a contentious relationship with China over trade practices, and these tariffs are just another chapter in that ongoing saga. As the world watches, it’s crucial to understand how this can impact not just businesses but everyday consumers as well.
Lesotho – 50%
Next on the list is Lesotho, facing a 50% tariff. This southern African nation is heavily reliant on textile exports to the U.S. market, and such a steep tariff could cripple its economy. For many workers in Lesotho, this translates to job losses and economic hardship. The U.S. has a history of providing trade preferences to African nations, but this move raises questions about future trade agreements.
With the textile industry being a significant employer in Lesotho, the effects of these tariffs could resonate throughout the region. It’s essential to keep an eye on the developments here, as they could set a precedent for how the U.S. engages with other African countries moving forward.
Cambodia – 49%
Cambodia is another country hit hard, with a tariff of 49%. Much like Lesotho, Cambodia’s economy is also tied to textile exports. The U.S. market is crucial for Cambodia’s growth, and this tariff could lead to a significant downturn in its economic prospects. It’s a challenging situation, and many are concerned about the broader implications for workers and families who depend on this industry.
As these tariffs take hold, there could be increased pressure on the Cambodian government to negotiate better terms or find alternative markets. The future of Cambodian exports hangs in the balance, and the international community will be watching closely.
Laos – 48%
Laos follows closely with a 48% tariff. This Southeast Asian nation has been working to diversify its economy, but the burden of such a high tariff could stifle its progress. With a focus on agriculture and energy exports, Laos may need to pivot its strategies to mitigate the impact of these tariffs.
The implications for Laos are significant. The country has been trying to attract foreign investment and develop its infrastructure, but with tariffs like these, it could deter potential investors and partners. It’s a delicate balance, and the government will have to navigate these waters carefully.
Madagascar – 47%
Madagascar is facing a 47% tariff, which could jeopardize its agricultural export markets. As a nation rich in biodiversity, it relies on exports like vanilla and seafood. The higher tariffs could lead to increased prices for U.S. consumers and reduced market access for Malagasy farmers and producers.
In a global economy that thrives on trade, Madagascar’s situation highlights the challenges faced by smaller nations when dealing with larger economies like the U.S. It’s a tough spot to be in, and one that requires careful handling to ensure that local communities are not adversely affected.
Vietnam – 46%
Vietnam is no stranger to tariffs, but a 46% increase is significant. The country has become a manufacturing hub in recent years, and this tariff could disrupt its burgeoning economy. Companies looking to invest in Vietnam may reconsider their options, which could lead to job losses and reduced economic growth.
For consumers in the U.S., this could mean higher prices on goods produced in Vietnam, from electronics to apparel. It’s a complicated situation that underscores the interconnectedness of global trade.
Myanmar – 44%
Myanmar faces a 44% tariff, adding to the challenges the country already faces. The political landscape in Myanmar has been tumultuous, and these tariffs could further complicate its economic recovery. The impact on exports could be severe, particularly for industries that are already struggling.
The international community has been watching Myanmar closely, and these tariffs may affect not just the economy but also the political dynamics within the country. It’s a situation that warrants attention, as the implications could be far-reaching.
Sri Lanka – 44%
Sri Lanka is in a similar boat, with a 44% tariff. The country has been working to recover from economic challenges, and this tariff could hinder its growth. With a focus on agriculture and textiles, Sri Lanka’s export market could take a hit, leading to potential job losses and economic instability.
As the global economy continues to evolve, Sri Lanka will need to adapt its strategies to navigate these challenges. The government may need to seek new trade agreements or bolster domestic industries to offset the effects of these tariffs.
Falkland Islands – 41%
The Falkland Islands, often in the news for political reasons, now find themselves with a 41% tariff. The islands primarily rely on fishing and tourism, and higher tariffs could hurt their economy. This situation highlights how even remote locations can be affected by global trade policies.
The future of the Falkland Islands’ economy may depend on finding new markets or diversifying their industries. As they navigate these changes, it will be essential to monitor their strategies and outcomes.
Syria – 41%
Syria is facing a 41% tariff as well, which complicates its already troubled economic situation. The ongoing conflict in the country has severely impacted its economy, and these tariffs could exacerbate existing challenges.
For Syria, the focus may need to shift towards rebuilding and finding new avenues for trade to help stabilize the economy. The international community’s response will be critical in determining the future of Syria’s trade relations.
Mauritius – 40%
Mauritius, known for its tourism and textile industries, is dealing with a 40% tariff. This could impact its economy, particularly as it tries to recover from the effects of the pandemic. The country has been working to diversify its economy, but these tariffs present a significant hurdle.
As Mauritius looks to navigate these challenges, it will be essential for the government to engage with international partners and seek out new trade opportunities. The success of these efforts will play a crucial role in the nation’s economic recovery.
Iraq – 39%
Iraq faces a 39% tariff, which complicates its efforts to rebuild its economy. The country has been working to stabilize and grow its markets, and these tariffs could hinder those efforts. For Iraq, it’s crucial to find ways to engage with other markets and diversify its economic base.
The international community will be watching closely to see how Iraq adapts to these tariffs and what strategies it implements to ensure economic growth and stability.
Guyana – 38%
Finally, Guyana is seeing a 38% tariff. This South American nation has been on the rise, particularly with its oil discoveries, but higher tariffs could impact its growth trajectory. As Guyana looks to develop its economy further, it may need to navigate these tariffs carefully to ensure continued progress.
The global economy is always in flux, and these tariffs are a reminder of how interconnected we all are. As we watch these developments unfold, it’s essential to consider the broader implications for trade, economics, and international relations. The effects of U.S. tariffs will undoubtedly resonate far beyond the borders of the countries involved, shaping the landscape of global trade for years to come.
