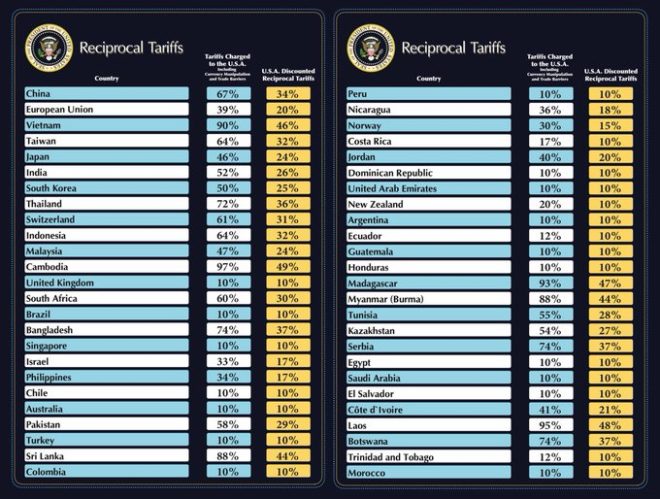
Overview of Trump Tariffs by Country
In April 2025, a tweet from Breaking911 highlighted significant tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, showcasing the economic implications of trade policies. This summary delves into the details of these tariffs, their impact on international trade, and the broader implications for both the U.S. economy and its trading partners.
Understanding Tariffs and Their Economic Impact
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on imported goods, aimed at making domestic products more competitive by raising the price of foreign goods. The Trump administration implemented various tariffs as part of its "America First" trade policy, which sought to protect American industries and reduce trade deficits.
The Rationale Behind Trump Tariffs
The primary rationale for the tariffs was to encourage domestic production and protect American jobs in sectors like steel, aluminum, and manufacturing. By making foreign goods more expensive, the administration aimed to incentivize consumers to purchase domestic products, thus stimulating the U.S. economy.
Key Countries Affected
The tweet from Breaking911 included a visual representation of the countries most affected by these tariffs. Key countries included:
- YOU MAY ALSO LIKE TO WATCH THIS TRENDING STORY ON YOUTUBE. Waverly Hills Hospital's Horror Story: The Most Haunted Room 502
- China: As one of the most significant trade partners of the United States, China faced substantial tariffs on various goods, particularly in the technology and agriculture sectors.
- Canada and Mexico: Neighboring countries with strong trade ties also encountered tariffs, particularly on steel and aluminum, which affected industries like automotive manufacturing.
- European Union: The EU faced retaliatory tariffs on a range of products, including agricultural goods and luxury items, as tensions escalated between the two economic powerhouses.
Economic Consequences
The implementation of these tariffs led to various economic consequences, both positive and negative.
Positive Aspects
- Increased Domestic Production: Some industries experienced a boost in production as tariffs made imported goods less competitive.
- Job Creation: Certain sectors, particularly manufacturing, saw a temporary increase in job opportunities as companies ramped up domestic production to meet consumer demand.
Negative Aspects
- Higher Consumer Prices: Consumers faced increased prices for various goods as the cost of imported products rose. This inflationary pressure affected household budgets and consumer spending.
- Retaliatory Measures: Countries affected by the tariffs often retaliated with their own tariffs, leading to a trade war that impacted American exporters, particularly in agriculture and manufacturing.
The Political Landscape
The tariffs were not only an economic tool but also a significant aspect of Trump’s political strategy. By appealing to his base, particularly in manufacturing-heavy states, Trump leveraged tariffs to solidify support among voters who felt left behind by globalization.
Bipartisan Reactions
While some lawmakers supported the tariffs, viewing them as necessary to protect American jobs, others criticized them for their potential negative impact on consumers and international relations. The trade policy became a contentious issue in American politics, with debates centering around free trade versus protectionism.
International Reactions
The global response to Trump’s tariffs varied, with some countries seeking to negotiate new trade agreements to mitigate the impact. Others engaged in discussions to diversify their trade relationships, reducing dependency on the U.S. market.
Long-term Implications
As the world navigates the complexities of international trade, the long-term implications of the Trump tariffs remain a topic of discussion among economists and policymakers. Understanding the impact of these tariffs is essential for predicting future trade dynamics and economic policies.
Conclusion
The Trump tariffs represent a significant chapter in the ongoing narrative of U.S. trade policy. Their implications extend beyond immediate economic effects, influencing international relations, domestic politics, and consumer behavior. As the global economy continues to evolve, the lessons learned from these tariffs will shape future trade negotiations and economic strategies.
In summary, tariffs can serve as both a protective measure for domestic industries and a source of tension in international trade relations. The analysis of Trump’s tariffs by country provides valuable insight into the complexities of trade policy and its far-reaching effects on economies worldwide. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and consumers as they navigate the ever-changing landscape of global trade.

TRUMP TARIFFS BY COUNTRY pic.twitter.com/R6uV1mBHUC
— Breaking911 (@Breaking911) April 2, 2025
TRUMP TARIFFS BY COUNTRY
When we talk about tariffs, especially those initiated during the Trump administration, it’s essential to understand their implications on trade and the global economy. Tariffs are essentially taxes imposed on imported goods, affecting both consumers and businesses. This article dives into the specifics of the Trump tariffs by country, exploring how they were structured and their lasting impact.
Understanding Tariffs: What They Are and Why They Matter
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of the tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, let’s clarify what tariffs are. Tariffs are government taxes on the importation of goods from other countries. They’re often used to protect domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive, thus encouraging consumers to buy local products. In the context of the Trump tariffs, these were often justified as necessary measures to protect American jobs and industries.
TRUMP TARIFFS BY COUNTRY: An Overview
During Donald Trump’s presidency, a significant number of tariffs were implemented, affecting various countries and industries. According to a recent [Breaking911 tweet](https://twitter.com/Breaking911/status/1907534353338614038?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw), these tariffs were applied unevenly across different nations, reflecting the administration’s strategic focus on trade imbalances and unfair practices.
Countries like China, Canada, Mexico, and members of the European Union were particularly targeted, each facing different rates and types of tariffs. For instance, the tariffs on steel and aluminum were among the most contentious, sparking debates about national security and economic stability.
The Impact of Tariffs on China
China was at the forefront of the tariff wars. The Trump administration imposed tariffs that exceeded 25% on numerous Chinese imports, which was part of a broader strategy to address what was perceived as unfair trading practices. A report by the [Council on Foreign Relations](https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/us-china-trade-war) noted that these tariffs were aimed at reducing the trade deficit and curbing intellectual property theft.
However, the impact was felt on both sides. While American manufacturers hoped to benefit from reduced competition, consumers faced higher prices for electronics, clothing, and other goods that were heavily reliant on Chinese imports. The trade tensions ultimately led to retaliatory tariffs from China, affecting U.S. exports like soybeans and automobiles.
Canada and Mexico: Neighbors in the Crossfire
Canada and Mexico, as part of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), were also significantly affected by the Trump tariffs. Initially, the tariffs on steel and aluminum were imposed on these countries as well, which strained relationships that were meant to be collaborative. According to the [Office of the United States Trade Representative](https://ustr.gov/countries-regions/americas/canada) (USTR), the tariffs were justified as necessary for national security.
In response, both Canada and Mexico implemented their own tariffs on American goods, which led to a complicated cycle of retaliation. The uncertainty caused by fluctuating tariffs also impacted businesses operating across North America, leading to calls for renegotiation of trade agreements.
European Union: A Complex Relationship
The European Union (EU) was not immune to the effects of Trump’s tariffs. With tariffs imposed on products like French wine and German automobiles, the EU responded with tariffs on iconic American products, including bourbon and motorcycles. This back-and-forth highlighted the delicate balance of transatlantic trade relations. According to a [report by the European Commission](https://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/countries-and-regions/countries/united-states/), the EU sought to protect its interests while advocating for a fair and balanced trading environment.
Domestic Reactions and Economic Impact
Domestically, the reaction to Trump’s tariffs was mixed. Some American workers, particularly in the steel and aluminum industries, celebrated the protective measures, believing they would secure jobs and bolster local economies. On the flip side, many economists warned that these tariffs could lead to job losses in sectors reliant on imported materials and products. A study by the [National Association of Manufacturers](https://www.nam.org/) projected that tariffs could lead to increased costs for manufacturers, which ultimately trickled down to consumers.
Long-Term Effects of the Tariffs
As we assess the long-term effects of the Trump tariffs, it’s vital to consider both immediate and future implications. The tariffs sparked discussions about the future of globalization, trade agreements, and economic policy. Some experts argue that the tariffs have led to a reevaluation of supply chains, pushing companies to diversify their sourcing strategies. This shift could potentially lead to a more resilient economy, but it also poses challenges as businesses navigate increased costs and regulatory complexities.
Global Trade Dynamics Post-Trump
Post-Trump, the landscape of global trade continues to evolve. New administrations often take varying approaches to tariffs and trade agreements. The Biden administration, for instance, has indicated a desire to collaborate with allies to address trade issues, particularly with China. Observers are watching closely to see how these shifts will impact existing tariffs and international trade relationships.
Conclusion: The Future of Tariffs and Trade
While the Trump tariffs were a significant chapter in American trade policy, they opened up broader conversations about the future of trade and tariffs. As nations continue to grapple with the implications of these policies, it’s clear that the world of trade is continuously evolving. Understanding the complexities of tariffs by country is crucial, not only for policymakers but for consumers and businesses alike. As we look ahead, it remains to be seen how these economic strategies will shape our global marketplace.
